Are you still wondering which transformer to choose in your factory? Are you still not sure about the types of transformers? This article provides you with a comprehensive understanding of the transformers types according to 10 different types of transformers. Let’s hurry up and get started!
Figure 0-0 use the image to determine the type of transformation shown
Types of Transformers: By Application
If we classify transformers according to their application, it can help engineers and technicians quickly choose the one that best meets the actual needs of their own factories. This will help us efficiently process the safety factor, work efficiency, and reliability of the system. You must understand clearly how a transformer works and what is a transformer used for.
Electrical transformer
Power transformers are divided into step-up and step-down transformers.
Step-Up Transformers
A step-up transformer means that it will step up a lower voltage to a higher voltage when transporting electricity.
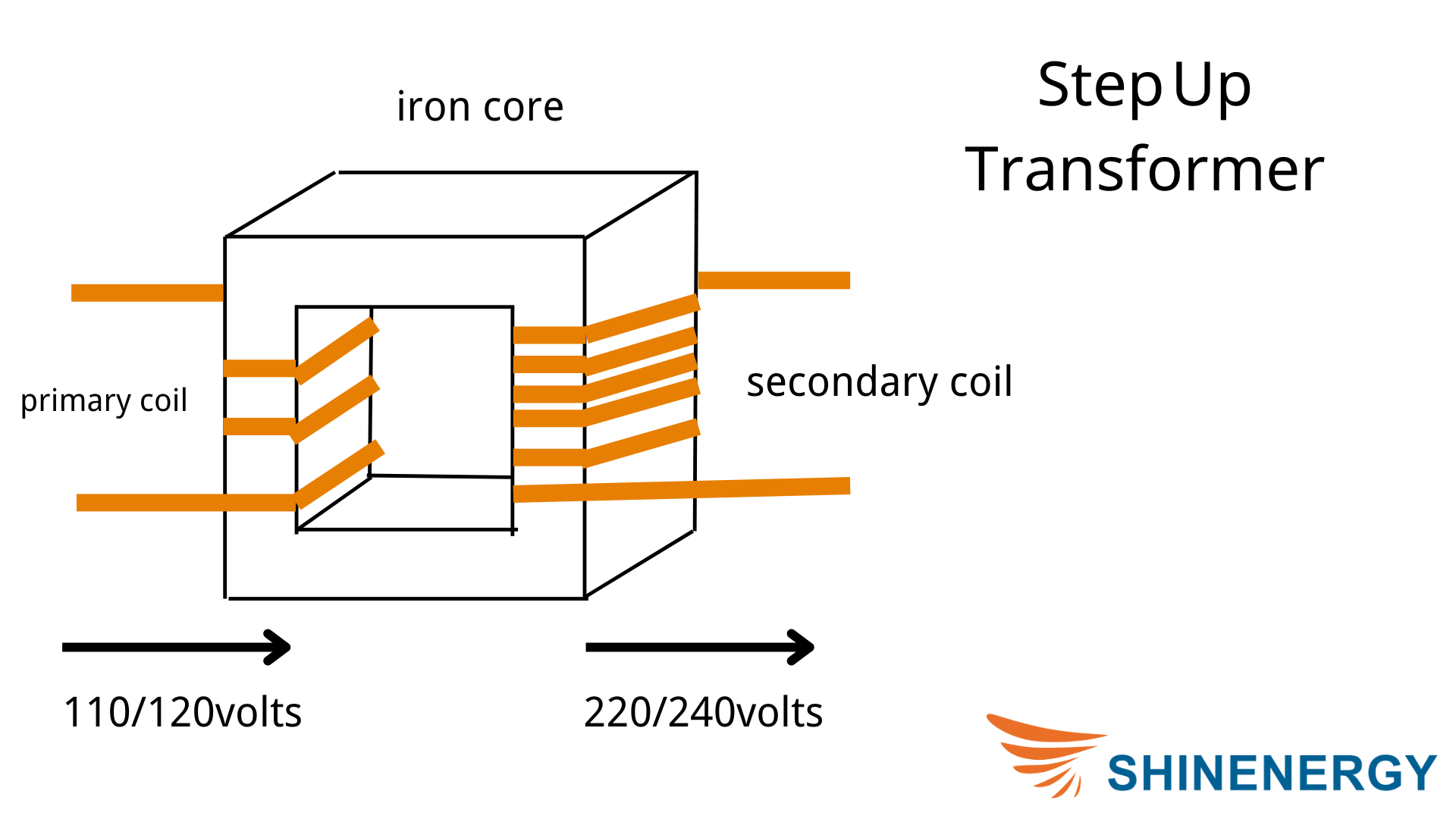
Figure 1-1 The amount of coils in primary winding and secondary winding is different
Step-Down Transformers
A step-down transformer means that it will reduce a higher voltage to a lower voltage when transporting electricity.
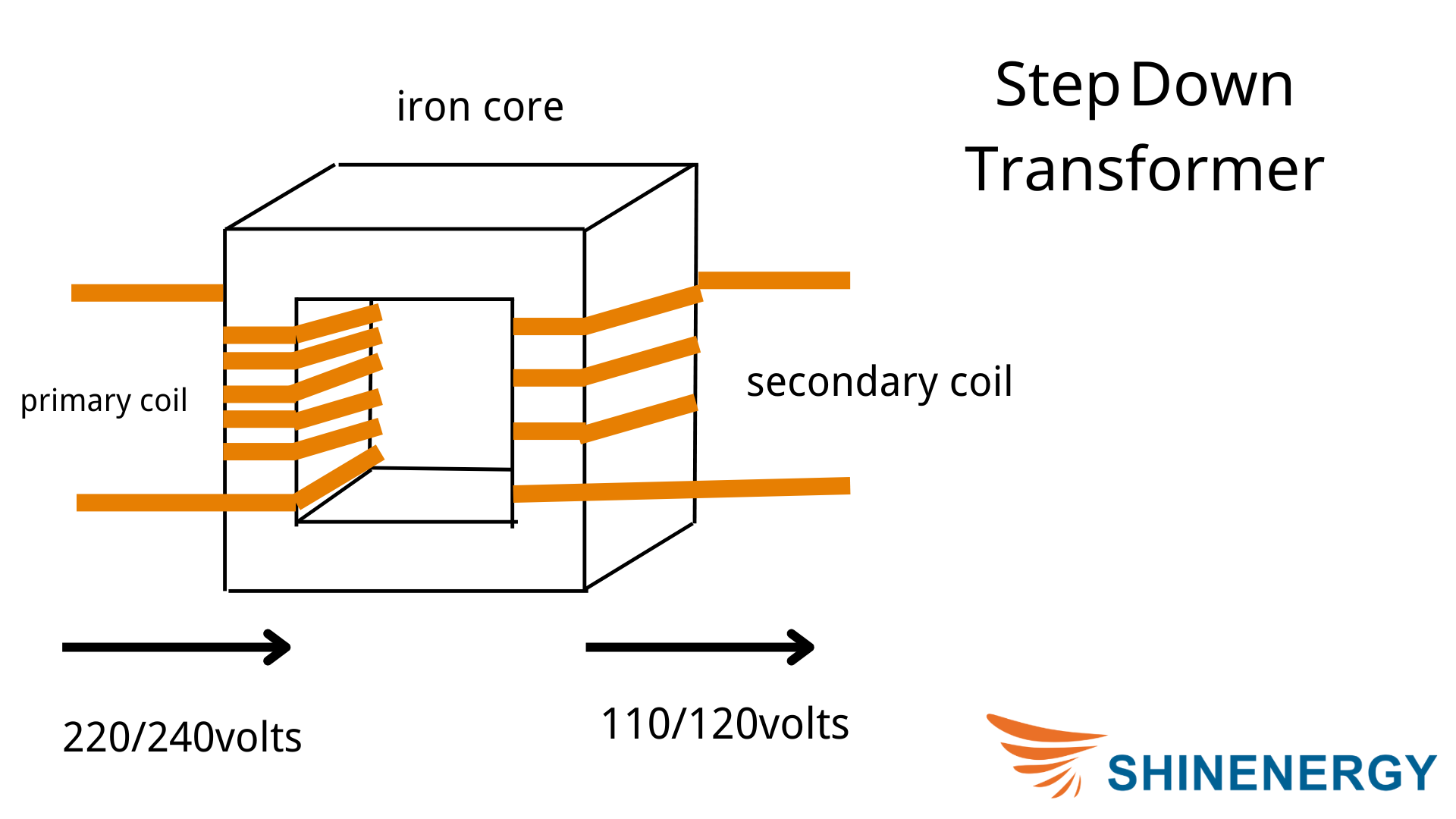
Figure 1-2 step-up transformers
Distribution Transformers
The distribution transformer is a key part of the entire power transmission system. It reduces the voltage of high-voltage power in the distribution system to the voltage level required by users through its own action.

Figure 1-3 Distribution Transformers
Dry-Type Distribution Transformers
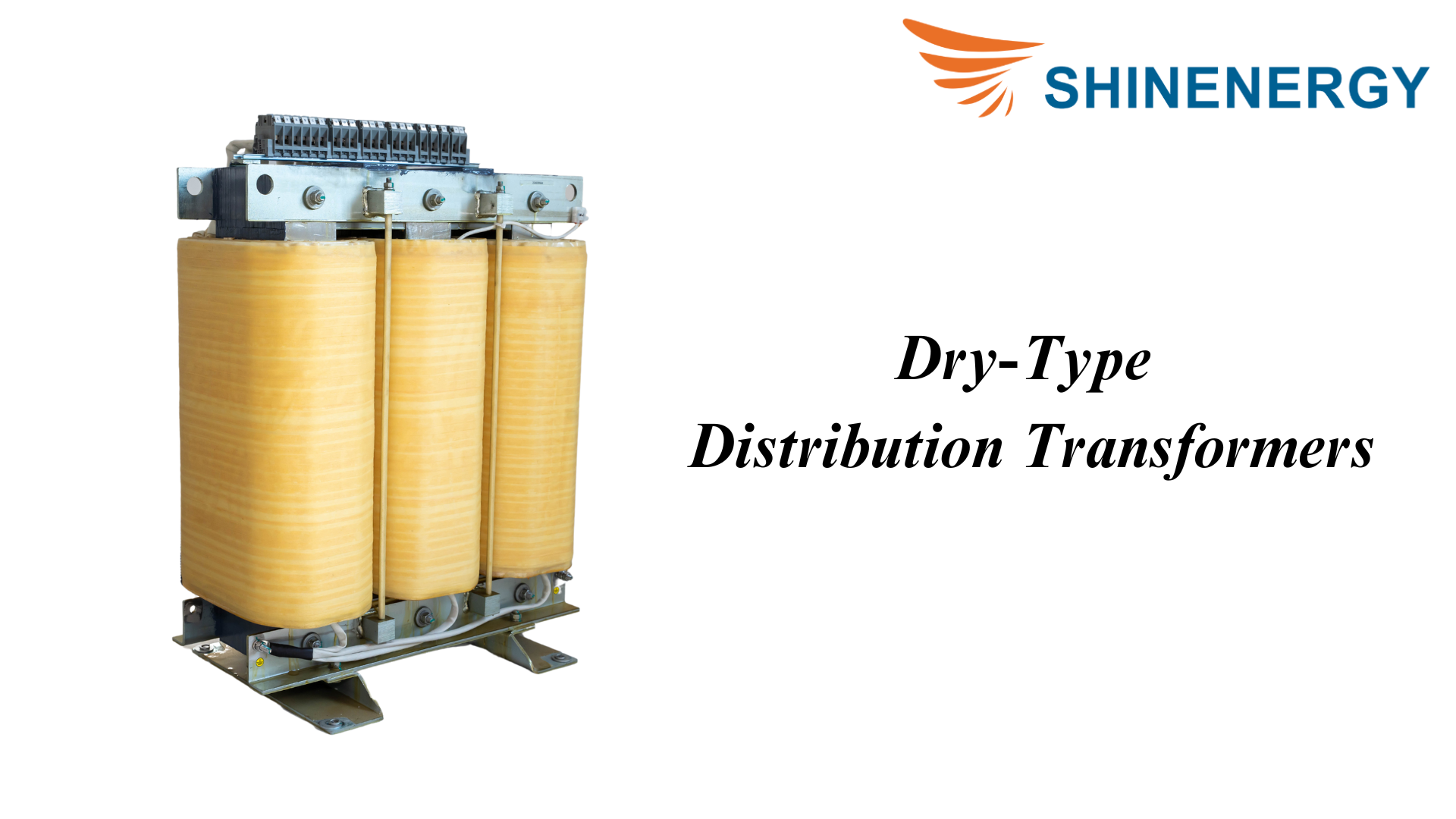
Figure 1-4 Dry-Type Distribution Transformers
A dry-type distribution transformer is a transformer that mainly relies on air or a specially designed cooling system to dissipate heat and does not require the use of oil for cooling. Compared with traditional oil-immersed transformers, dry-type transformers are safer because there is no risk of oil leakage and fire. So, do you know the types of dry-type transformers?
Oil-Immersed Distribution Transformers

Figure 1-5 Oil-Immersed Distribution Transformers
Oil-immersed distribution transformers immerse the windings and cores in transformer oil to exert insulation properties and dissipate heat. As its name suggests, it is a transformer that uses oil for insulation and cooling.
Industrial Control Transformers

Figure 1-6 Industrial Control Transformers
An industrial control transformer is a transformer specially designed for industrial environments. Because it provides a stable low-voltage power supply, it can ensure the normal operation of machines and control systems.
Isolation Transformers

Figure 1-7 Isolation Transformers
Isolation transformer is a transformer widely used to separate equipment and power supply in power systems. Its purpose is to increase safety and reduce electrical noise and interference.
Autotransformers

Figure 1-8 Autotransformers
An autotransformer is a special type of transformer in which part of the windings are common, meaning there is an electrical connection between the primary and secondary windings. Autotransformers use less material than traditional transformers and are therefore generally smaller, lighter, and more economical.
Instrument Transformers

Figure 1-9 Instrument Transformers
This type of transformer is used to measure current, voltage, and electrical energy. They reduce high voltage or high current to safe and easy-to-measure levels, providing accurate measurement signals to instruments and protection equipment in the power system.
Current Transformers

Figure 1-10 Current Transformers
Current Transformers convert the large input current into a small output current in proportion, usually 5 amps or 1 amp, which facilitates measurement and protection of equipment.
Voltage Transformers
Figure 1-11 Voltage Transformers
Voltage Transformers proportionally convert the input high voltage into the output low voltage, usually 100 volts or 110 volts, which facilitates measurement and protection of equipment.
voltage transformer application
Types of Transformers: By Phase
Transformers can be divided into single-phase and three-phase transformers. How many types of transformers are there?
Single-Phase Transformers

Figure 2-1 Single-Phase Transformers
Single-phase transformers are transformers used in single-phase AC power systems. Their main function is to convert voltage from one level to another to meet the needs of different equipment and systems. Single-phase transformers are widely used in residential, commercial, and small industrial locations.
Three-Phase Transformers
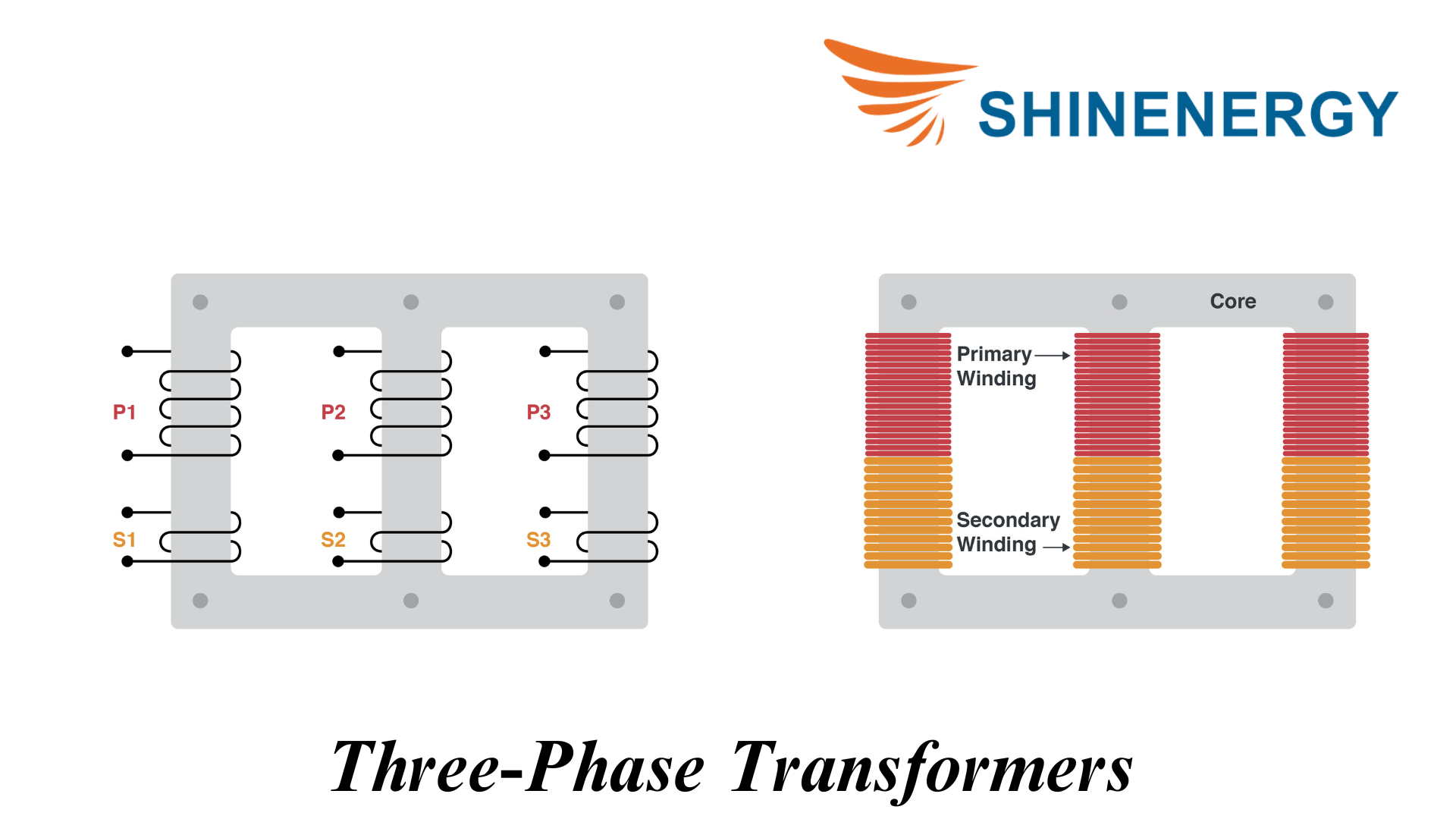
Figure 2-2 Three-Phase Transformers
Three-phase transformers are transformers used in three-phase AC power systems and are widely used in industrial, power transmission, and distribution systems. They can handle high power demands efficiently and stably.
Types of Transformers:By Core Structure
By the core type transformer, There are 4 types of transformation. Let’s begin to learn about the core type, shell type transformer, and so on.
Iron Core Transformers
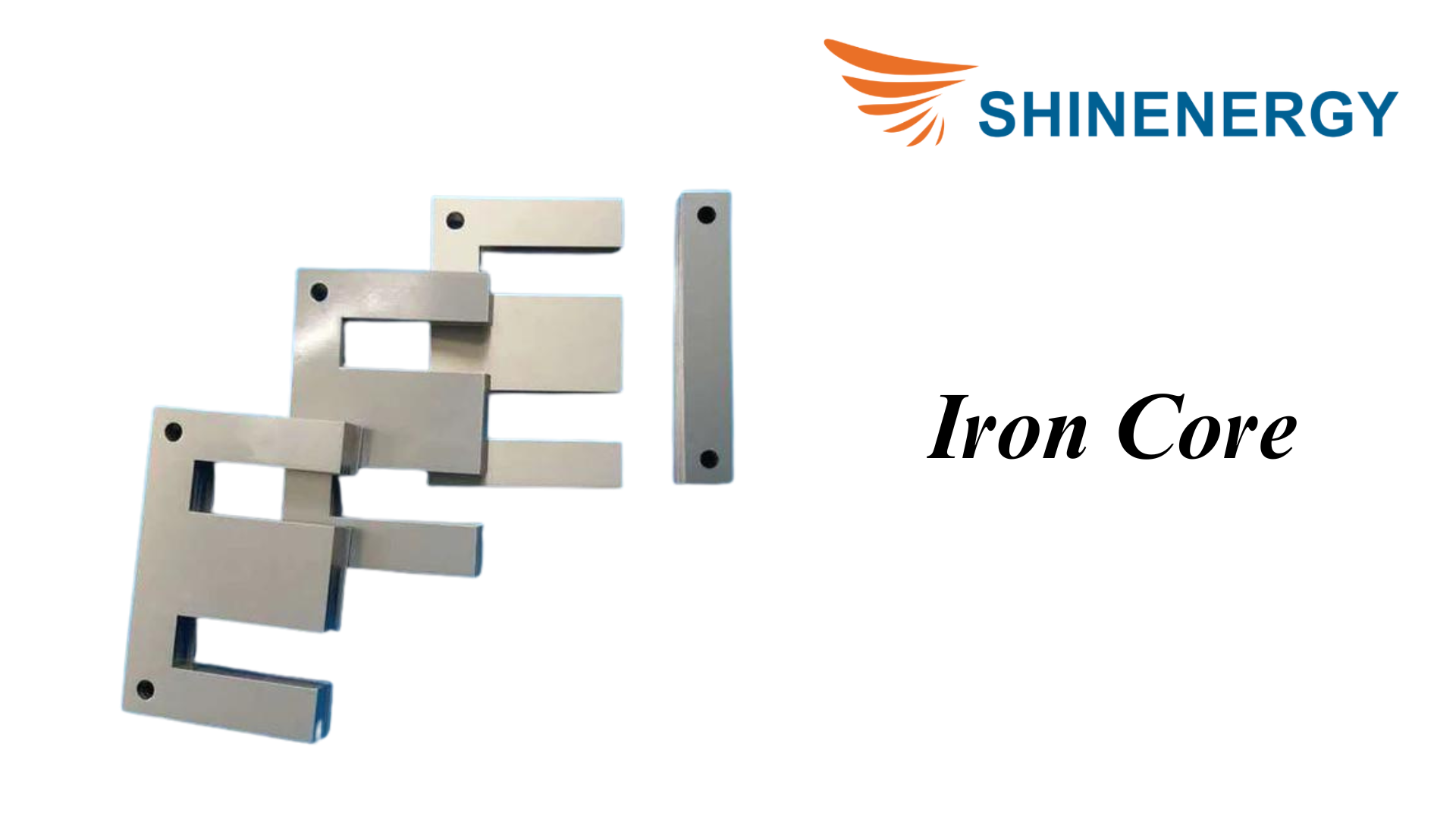
Figure 3-1 Iron Core Transformers
Iron core transformers utilize an iron core to conduct magnetic flux, thereby increasing efficiency and performance. It transfers energy between the primary winding and the secondary winding through a magnetic field. The use of an iron core greatly reduces magnetic losses and improves the efficiency of the transformer.
Air Core Transformers

Figure 3-2 Air Core Transformers
An air-core transformer is a transformer without an iron core and relies on air to conduct magnetic flux. They are mainly used in high-frequency applications and special occasions. Because there is no iron core, there is no hysteresis and eddy current loss, so they are more efficient at high frequencies.
Ferrite Core Transformers

Figure 3-3 Ferrite Core Transformers
A ferrite transformer is a transformer that uses ferrite material as its magnetic core. Because this material has high magnetic permeability and low loss, it is particularly suitable for high-frequency applications.
Toroidal Core Transformers

Figure 3-4 Toroidal Core Transformers
A toroidal transformer is a transformer that uses a toroidal magnetic core. This kind of magnetic core is usually made of iron powder, ferrite, or other magnetic materials and has high magnetic permeability and low loss. Due to its unique structure and superior performance, toroidal transformers are widely used in various power and electronic equipment.
Types of Transformers:By Voltage Regulation
The efficiency and load capacity of the electrical system largely depend on the KVA rating of the transformer used in the circuit.
On-Load Tap Changing Transformers

Figure 4-1 On-Load Tap Changing Transformers
An on-load regulating transformer (OLTC) is a transformer that can adjust the output voltage when there is a load. By changing the tap position of the transformer winding, OLTC is able to regulate the voltage without interrupting the power supply, maintaining the stability of the power system and the optimization of voltage levels.
Off-Load Tap Changing Transformers

Figure 4-2 Off-Load Tap Changing Transformers
An off-load regulating transformer (OLTC) can only adjust voltage when there is no load. In contrast, unlike the on-load voltage regulating transformer, the unloaded voltage regulating transformer requires manual or automatic adjustment of the tap of the winding to change the output voltage when no current flows through the transformer.
Types of Transformers:By Application Environment
The Indoor and outdoor transformer bring different advantages of transformer
Indoor Transformers

Figure 5-1 Indoor Transformers
Indoor transformers are transformers specially designed for use in indoor environments
Outdoor Transformers
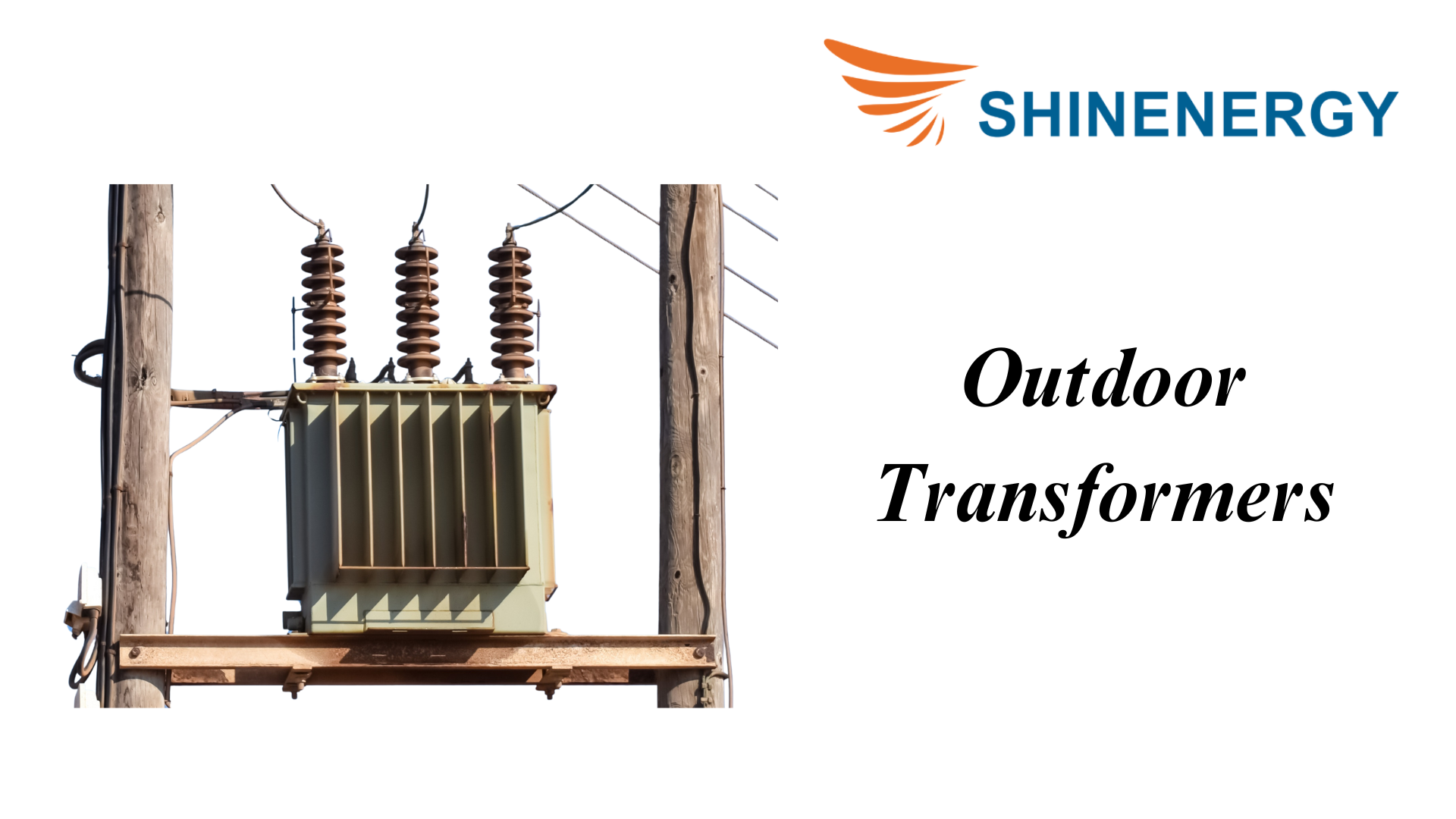
Figure 5-2 Outdoor Transformers
Indoor transformers are transformers specially designed for use in outdoor environments
Types of Transformers:By Cooling Method
By Cooling Method, there are 4 types of transformations, and different types of transformer bring different functions
Oil-Cooled Transformers

Figure 6-1 Oil-Cooled Transformers
Oil-cooled transformers use transformer oil as a cooling medium to take away the heat generated during the operation of the transformer through natural circulation or forced circulation. Oil-cooled transformers are widely used in high-voltage and large-capacity power transmission and distribution systems.
Air-Cooled Transformers

Figure 6-2 Air-Cooled Transformers
Air-cooled transformers use air as the cooling medium to dissipate heat to the surrounding environment through natural convection or forced ventilation. Air-cooled transformers are suitable for low and medium voltage and small and medium capacity applications.
Water-Cooled Transformers

Figure 6-3 Water-Cooled Transformers
Water-cooled transformers use water as the cooling medium to take away the heat generated by the transformer through the water circulation system.Water-cooled transformers suit specific industrial and power applications, especially where high cooling efficiency is required.
Gas-Cooled Transformers

Figure 6-4 Gas-Cooled Transformers
Gas-cooled transformers use gas as the cooling medium. They are widely used in high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage power systems, especially where efficient cooling and excellent insulation performance are required.Our catalog includes descriptions and specifications of the types of transformers available.
Types of Transformers:By Winding Arrangement
Two-Winding Transformers
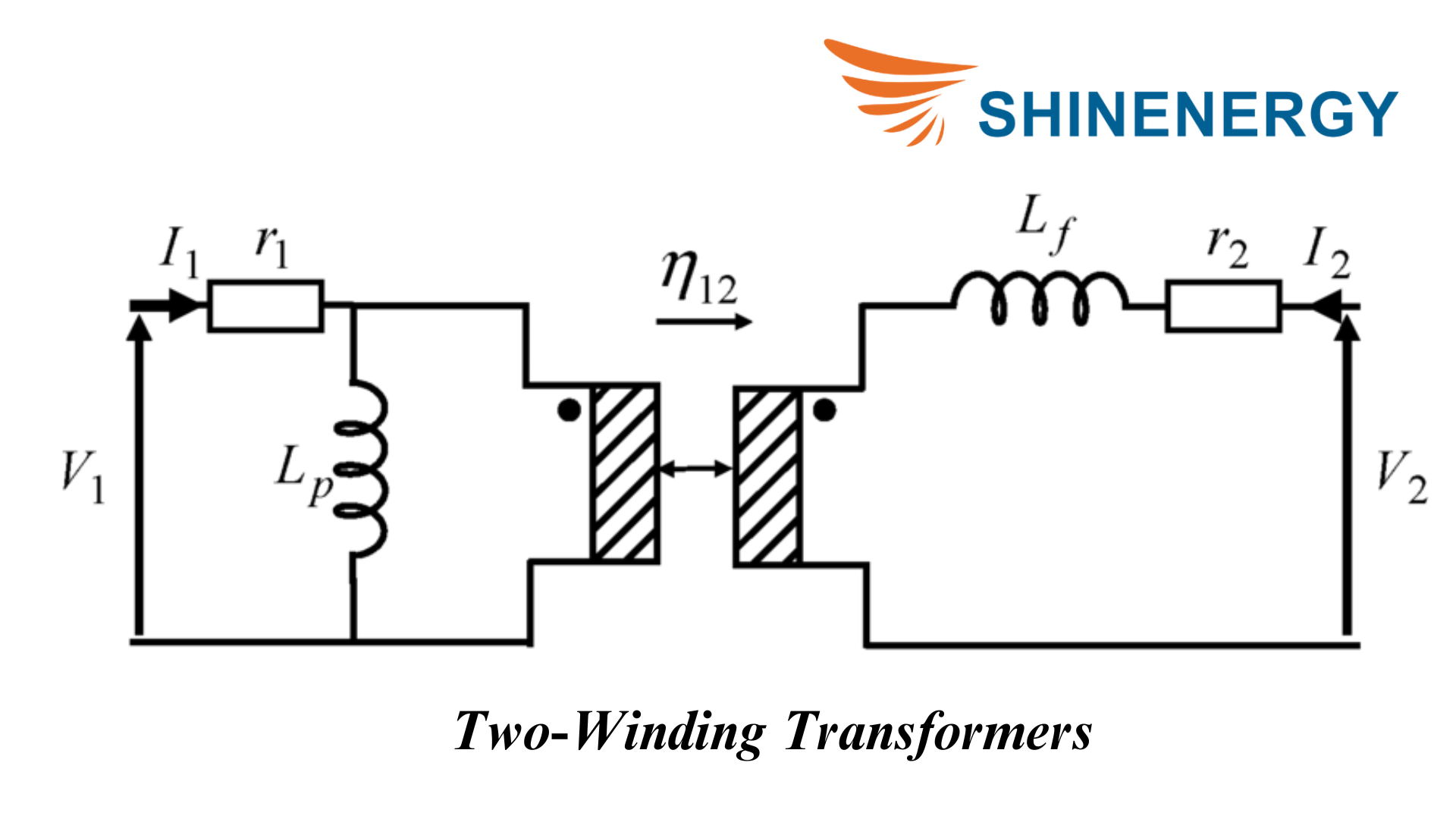
Figure 7-1 Two-Winding Transformers
Two-winding transformers are the most common type of transformer and have two separate windings: a primary and a secondary. They are used for voltage conversion and isolating two circuits.
Three-Winding Transformers
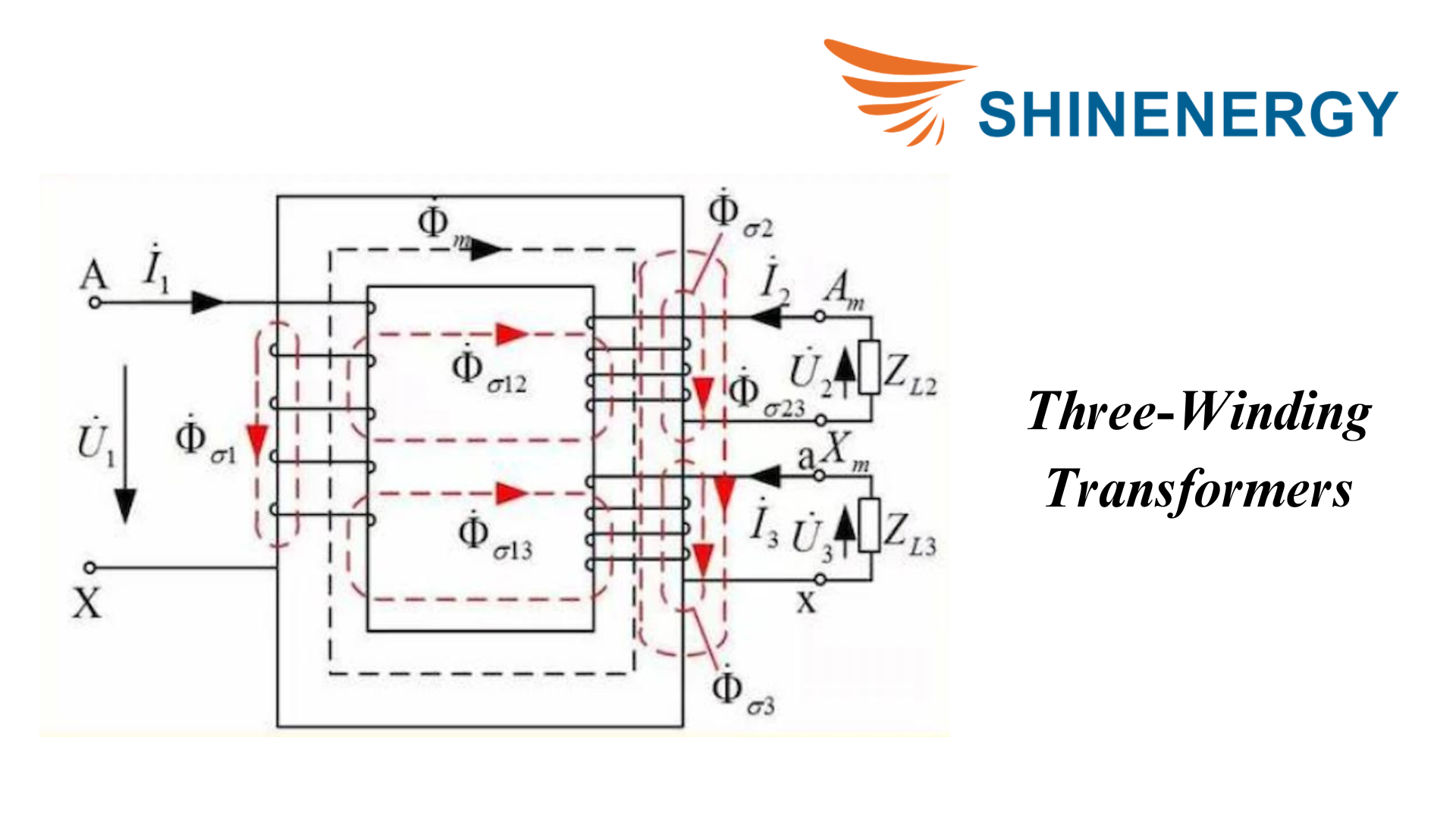
Figure 7-2 Three-Winding Transformers
Three-winding transformers have three separate windings, usually a primary winding and two secondary windings. They are used to convert one voltage level to two different voltage levels. Researchers study the performance of different types of transformers under various conditions.
Zigzag Transformers
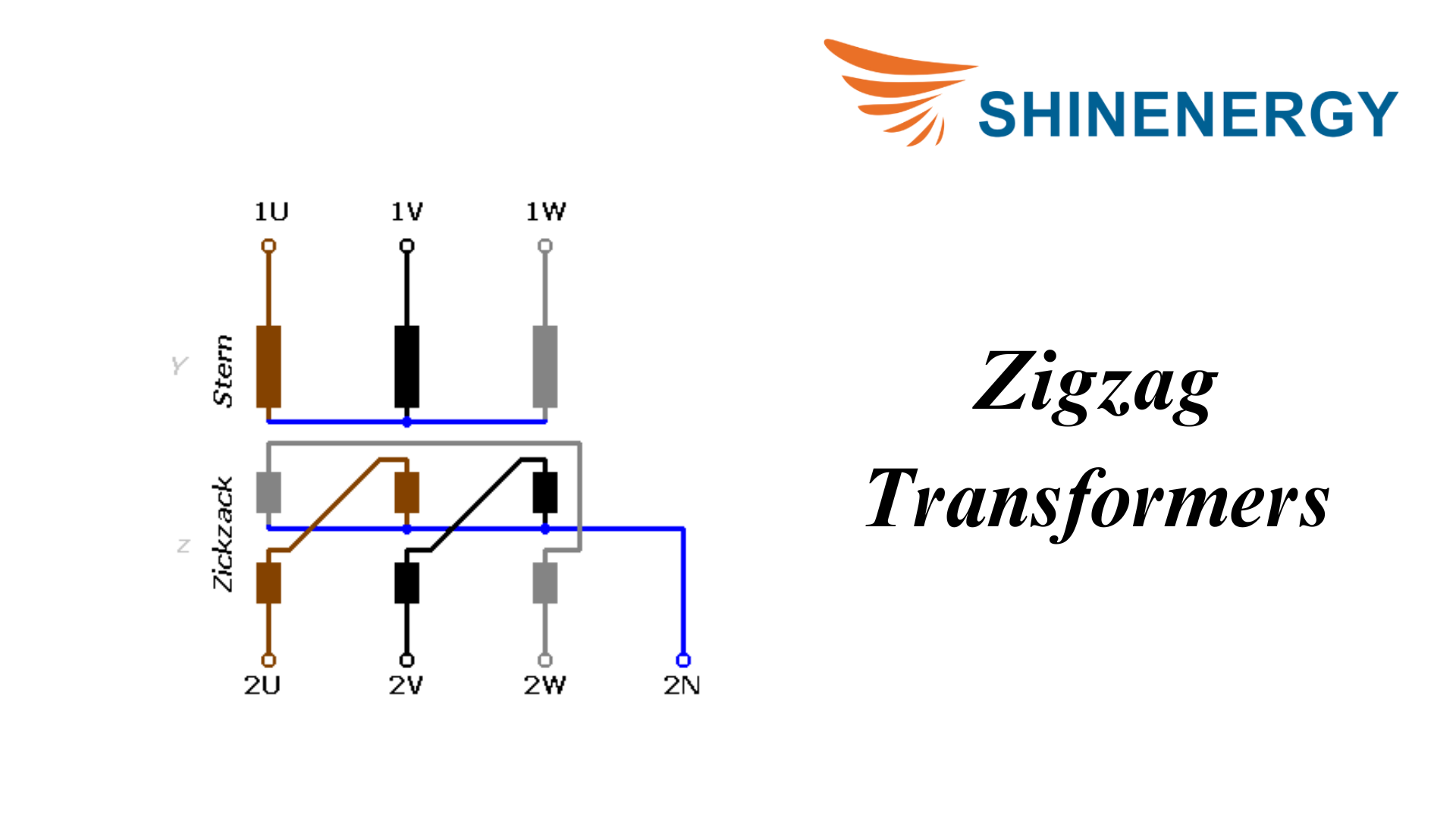
Figure 7-3 Zigzag Transformers
Z-type transformers are special transformers used for grounding, harmonic reduction, and balancing unbalanced loads in three-phase power systems. Their windings are configured in a Z shape, giving them unique electrical characteristics.The market offers various types of transformers for residential and commercial use.
Types of Transformers:By Frequency
What are the 3 types of transformers by Frequency?
Low-Frequency Transformers

Figure 8-1 Low-Frequency Transformers
Low-frequency transformers are mainly used for low-frequency power transmission and conversion, usually working in the frequency range of 50Hz to 400Hz. They are widely used in power transmission, industrial equipment, and household appliances.Designers select specific types of transformers based on the requirements of the circuit.
High-Frequency Transformers

Figure 8-2 High-Frequency Transformers
High-frequency transformers are used for high-frequency power conversion and signal processing, usually operating in the frequency range of several thousand Hertz (kHz) to several megahertz (MHz). They are widely used in electronic equipment and communication systems.
Audio Frequency Transformers

Figure 8-3 Audio Frequency Transformers
Audio transformers process and transmit audio signals, operating in the frequency range between 20Hz and 20kHz. They are widely used in audio equipment and communication systems.
Types of Transformers:By Special Application
General Purpose Transformers

Figure 9-1 General Purpose Transformers
A general-purpose transformer converts voltage from one level to another to meet the power needs of different devices and systems. It is suitable for various purposes.We will compare the efficiency of different types of transformers in today’s lecture.
Grounding Transformers and Earthing Transformers

Figure 9-2 Grounding Transformers and Earthing Transformers
Grounding transformers provide a grounding point to the power system, especially in systems without direct neutral grounding. They ensure the system’s safety and stability by creating an artificial neutral point in the power grid.Technicians must know the types of transformers to troubleshoot electrical systems effectively.
Rectifier Transformers

Figure 9-3 Rectifier Transformers
Rectifier transformers power rectifier equipment to convert AC power into DC power. They work with rectifiers to provide the required DC voltage and current.
RF Transformers
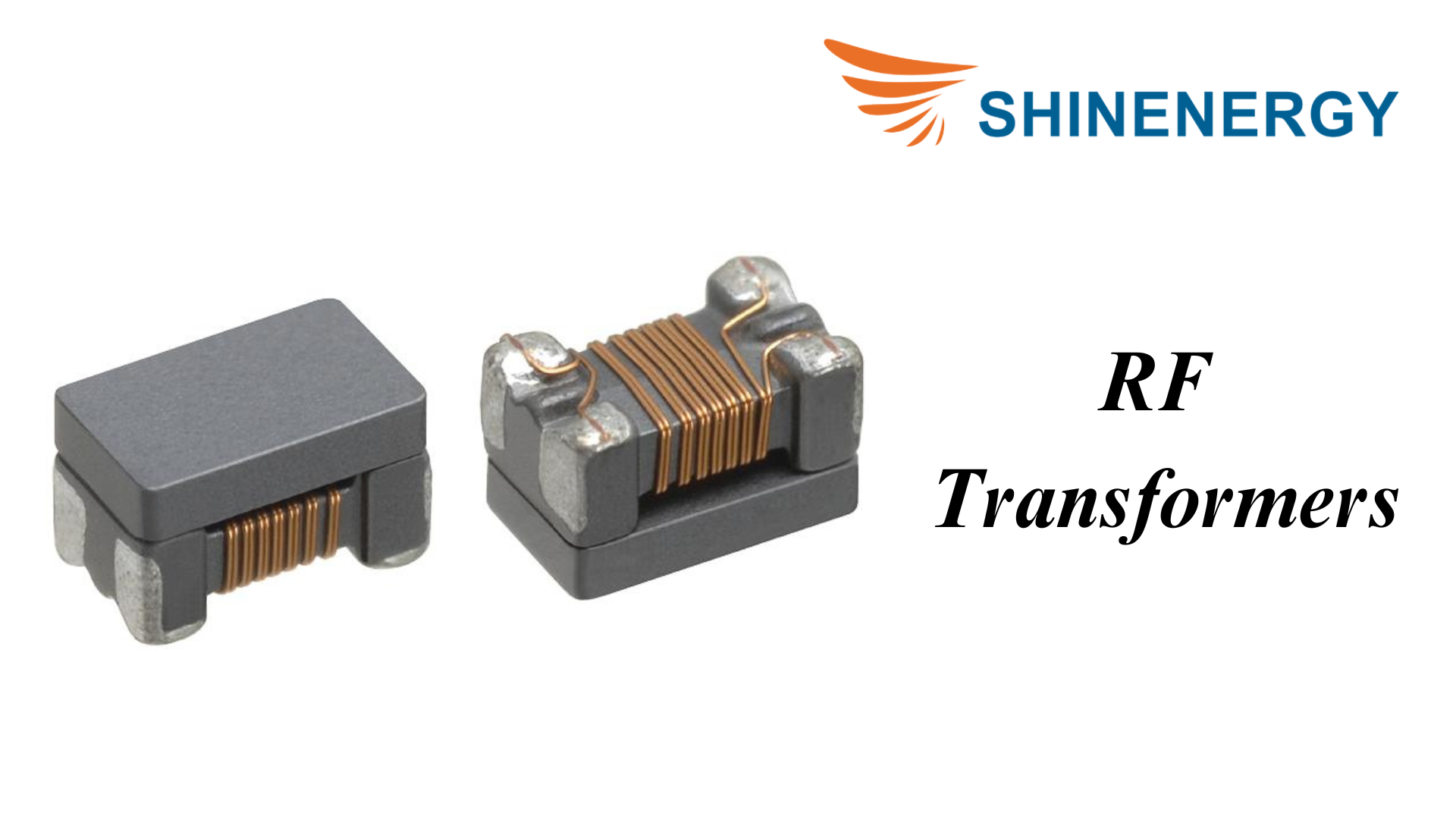
Figure 9-4 RF Transformers
RF transformers transmit and match high-frequency signals in RF circuits. They are widely used in communication equipment, broadcasting, and receiving equipment.Our course covers the types of transformers used in industrial applications.
Variable Transformers
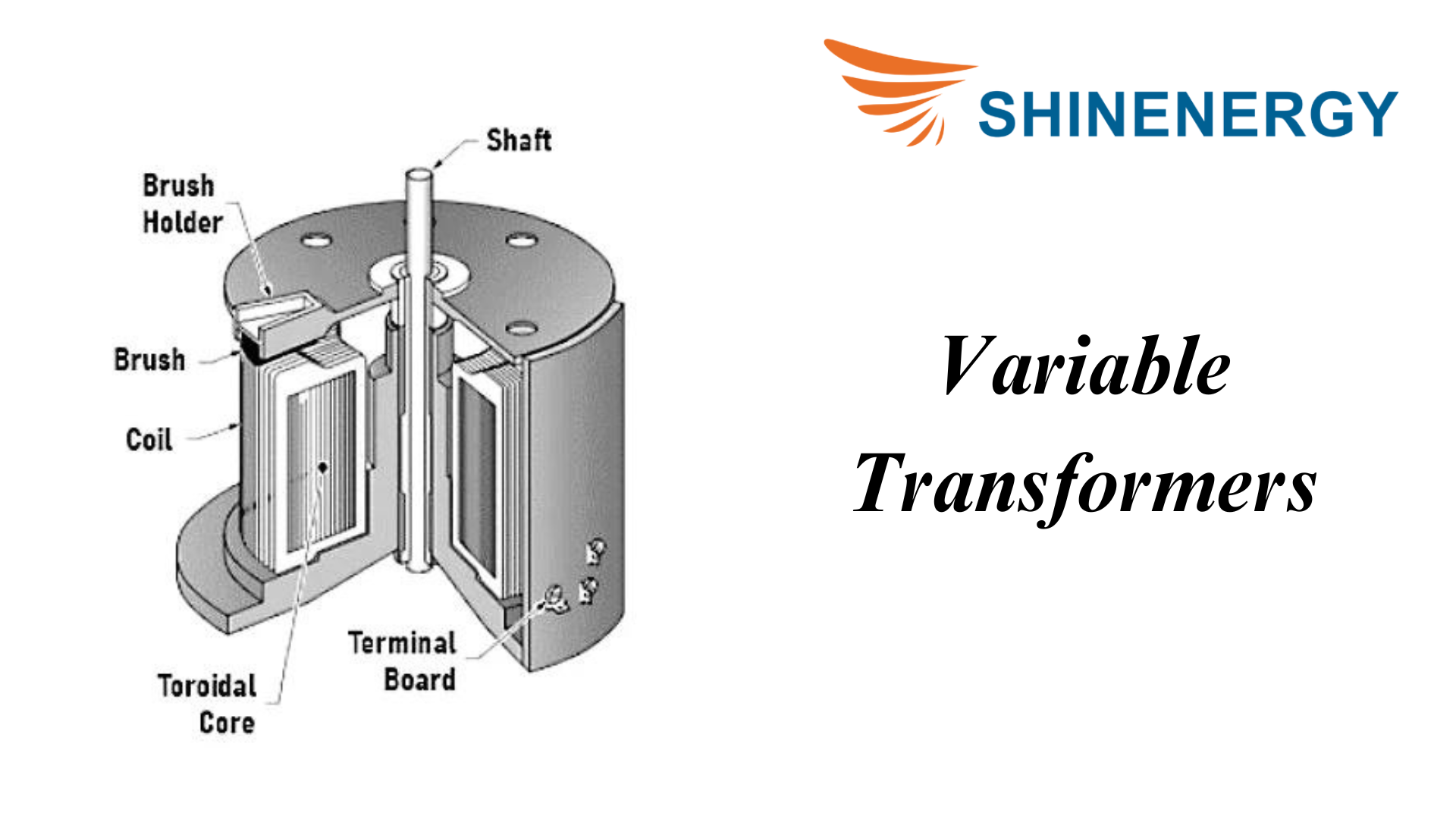
Figure 9-5 Variable Transformers
Variable transformers provide adjustable output voltage and are widely used in test equipment, laboratories, and control systems.
Impedance Matching Transformers
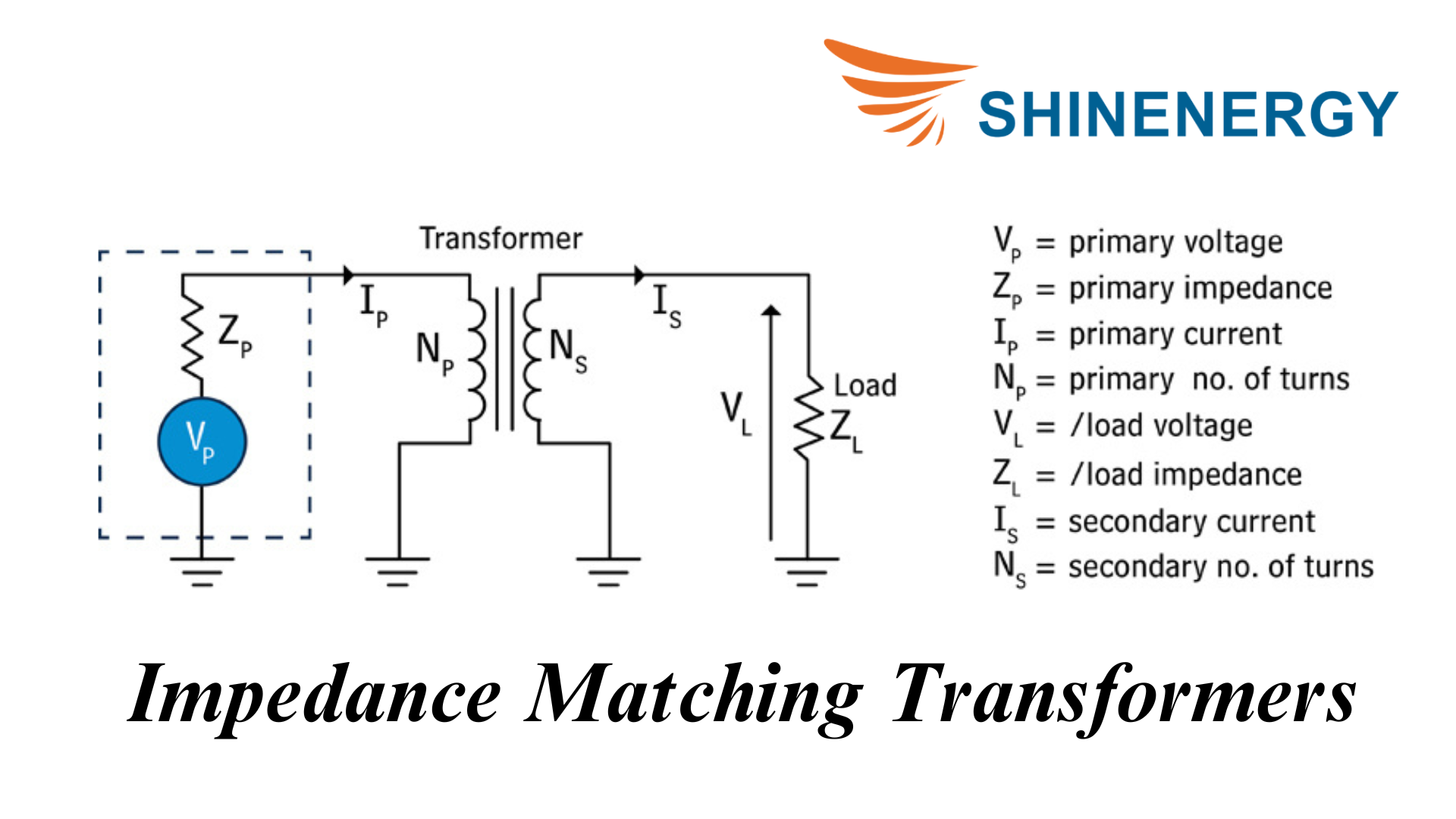
Figure 9-6 Impedance Matching Transformers
Impedance matching transformers provide optimal energy transfer between circuits of different impedances, reducing reflections and losses.Manufacturers produce several types of transformers to meet diverse electrical needs.
K-Factor Transformers

Figure 9-7 K-Factor Transformers
K-factor transformers handle non-linear loads with harmonics and often serve places with high power quality requirements, such as computer centers and data centers.We need to understand the various types of transformers for this project.
Power Electronic Transformers
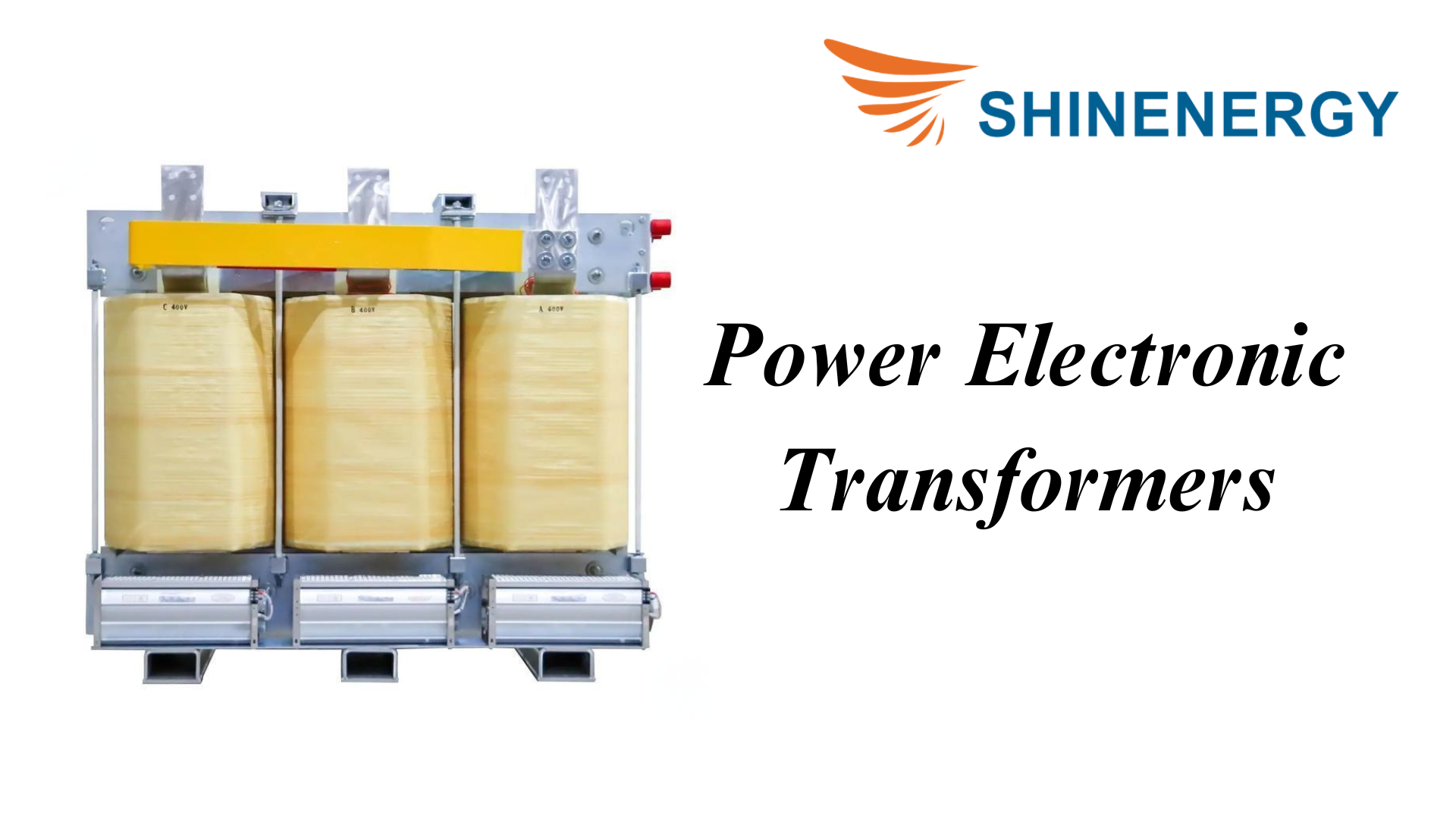
Figure 9-8 Power Electronic Transformers
Power electronic transformers use power electronics technology for efficient power conversion and transmission, and often operate in smart grid and renewable energy systems.Engineers classify the different types of transformers based on their specific functions.
conclusion
In electrical engineering, understanding the types of transformations and the types of transformer, such as the type of transformer used for specific applications, is crucial. It’s important to recognize the differences between each type of transformer and explore all types of transformers to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, studying the different types of transformations can provide deeper insights into their functionalities and applications
FAQ:
What are the parts of the transformer?
-The parts of a transformer include the core, windings (primary and secondary), insulation, transformer oil, bushings, conservator, and cooling fins or radiators.
Can you explain the working of a transformer and how it impacts the efficiency of electrical power distribution?
-A transformer works by using electromagnetic induction to convert voltages from one level to another. Specifically, it either steps up or steps down the voltage. Consequently, this impacts the efficiency of electrical power distribution by reducing energy loss during transmission, allowing for efficient long-distance power delivery.
How does the construction of a transformer affect its efficiency and performance in electrical power distribution systems?
-The construction of a transformer affects its efficiency and performance by determining how well it minimizes energy losses. High-quality materials for the core and windings, proper insulation, and effective cooling systems all contribute to reducing losses and enhancing performance in electrical power distribution systems.
Can you explain the working principle of a generator? In addition, what is the relationship between generators and transformers?
-The working principle of a generator involves electromagnetic induction, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil within a magnetic field.The relationship between generators and transformers is clear. Generators produce electrical energy, whereas transformers adjust the voltage of this electricity for efficient transmission and distribution.
Can you provide a transformer parts diagram to help illustrate its components?
-Core
-Primary winding
-Secondary winding
-Insulation
-Transformer oil
-Bushings
-Conservator
-Cooling fins/radiators
What unique features distinguish a Berry type transformer from other transformer types?
-The Berry-type transformer features a cylindrical core and distributed winding arrangement. Consequently, it provides better cooling and reduces magnetic losses compared to other transformer types.
What is the function of a transformer in a power supply system?
-A transformer in a power supply system changes the voltage level. Specifically, it either steps it up for long-distance transmission or steps it down for safe distribution and use.
-Of course, it is our honor to serve you. If you need relevant documents, please leave your contact information in the contact box on the right.


Pingback: Angthong National Marine Park
Pingback: clothing manufacturer
Pingback: suzuran168