Transformer insulation is one of the transformer components. Transformer insulation is the backbone of reliable and efficient operation. It ensures electrical safety, prevents failures, and enhances energy efficiency. By resisting thermal, mechanical, and electrical stresses, insulation helps transformers meet demanding performance requirements. Engineers who understand the latest materials and innovations can design systems that are not only safer but also more cost-effective, aligning with modern sustainability goals.

Figure 1 Vintage transformer cloth insulation
Overview of transformer insulation

Figure 1-1 Transformer cloth insulation
What is Transformer Insulation?
Different dry type transformer types will have different transformer insulation types Transformer insulation is a critical transformer insulation component that separates electrical currents while ensuring energy transfer efficiency. It prevents short circuits, enhances safety, and prolongs the lifespan of transformers. Materials like paper insulation transformer, oil, resin, and gas are commonly used.
The Role of Insulation in Transformer Performance
Insulation protects against electrical faults by withstanding high voltages. It also reduces energy loss during operation, ensuring transformers run efficiently even in extreme environments. A low insulation resistance of the transformer may indicate potential electrical problems. An insulation resistance test ofa transformer is essential for detecting possible insulation failures in advance.An insulation power factor test transformer should be done regularly to ensure the reliable operation of the electrical equipment.
Why Transformer Insulation Needs Innovation
Rising energy demands and sustainability goals push the need for eco-friendly, high-performance insulation materials. New technologies reduce maintenance costs while improving system durability.
Insulation class of dry type transformer insulation

Figure 1-2 insulation level of transformer
Dry type transformer insulation class and temperature rise:
- class A insulation transformer:105℃
- class E insulation transformer:120℃
- class B insulation transformer:130℃
- class H insulation transformer:155℃
- class C insulation transformer:180 and above℃
- class F insulation transformer:220℃
transformer insulation class chart
| Insulation Class | Temperature Limit (℃) | Commonly Used Insulation Materials |
| Class A | 105 | Cellulose materials treated by impregnation (such as insulation paper used in transformers, paperboard, etc.) |
| Class E | 120 | Polyester film, Polyester fiber paper, etc. |
| Class B | 130 | Mica, Fiberglass, etc. |
| Class F | 155 | Epoxy resin, Nomex paper, etc. |
| Class H | 180 and above | Silicone rubber, Ceramic fiber, etc. |
| Class C | 220 | Polyimide film, Mica products, and other high-temperature resistant materials |
transformer insulation class chart
Dry type transformer insulation materials
Figure 1-3 Transformer insulation material
- class A: Cellulose materials (cellulose cloth material)treated by impregnation (such as paper, paperboard, etc.)
- class E: Polyester film, Polyester fiber paper, etc.
- class B: Mica, Fiberglass, etc.
- class F: Epoxy resin, Nomex transformer insulation paper, etc.
- class H: Silicone rubber, Ceramic fiber, etc.
- class C: Polyimide film, Mica products, and other high-temperature resistant materials
Types of insulation used in transformer

Figure 2-1paper cellulose insulation
The type and quality of transformer insulation play a significant role in determining the overall transformer quotation. High-performance and advanced insulated materials usually lead to a higher price for the transformer.
types of dry type transformer Insulation: Solid Insulation

Figure 2-2 dry type transformer insulation
Solid insulation materials like cellulose vintage transformer paper have been widely used for a long time. paper cellulose insulation in transformers offers good transformer cloth insulation properties and is relatively inexpensive. It is often used in combination with oil in oil immersed transformer. In recent years, there have been advances in the treatment of cellulose insulating paper for transformers to make it more resistant to moisture and aging. For example, some manufacturers are using special coatings or impregnation techniques to enhance its durability.
Another solid insulation material for transformer is mica. Mica has excellent thermal stability and dielectric strength. It is commonly used in high-temperature and high-voltage applications, such as in some large power transformer insulation in power plants. Mica tape is wrapped around the windings to provide insulation that can withstand the harsh conditions inside the transformer during operation.
Applications of solid insulation vary from small distribution transformers to large power transformers. In distribution transformers, solid insulation helps in maintaining electrical safety at the local level where the voltage is stepped down for household and small business use. In power transformers, it plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable operation under high voltages and heavy loads.
Types of transformers insulation: Liquid Insulation transformer

Figure 2-3 Liquid Insulation
Dielectric fluids such as mineral oil are vital in liquid filled transformers. Mineral oil provides good electrical insulation and also acts as a coolant. This product isn’t made with food grade mineral oil. liquid filled transformers circulates inside the transformer, carrying away heat generated by the windings and core, and helping to keep temperatures within acceptable limits to ensure that the transformer insulator and other components work properly.
However, the maintenance of liquid insulation requires regular attention. transformer insulating oil quality needs to be monitored regularly through tests such as Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA). If the oil becomes contaminated with moisture, particles or other impurities, its insulating properties will deteriorate. In this case, the insulating oil in transformer may need to be filtered or replaced. Regular visual inspections of the transformer tank for leaks as well as ensuring proper oil levels are also important aspects of liquid insulation maintenance.
Another increasingly favoured liquid insulation is natural ester oils. They are more environmentally friendly than mineral oils because they are biodegradable. And in some cases, they also have better fire resistance, making them a viable option for transformers installed in areas where fire safety is a requirement.
Gas Insulation transformer: Unique advantages in specific environments

Figure 2 gas-insulated transformer market
Gas insulated transformer, particularly sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), offers several unique advantages. sf6 gas insulated transformer has very high dielectric strength, which means that it can withstand very high voltages without breakdown, and is chemically stable under normal operating conditions. This makes it ideal for high-voltage gas-insulated switchgear as well as for some specialised transformers in power transmission systems.
At the gasinsulated transformer market, Gas-insulated transformers using SF6 can be installed in compact substations where space is limited. The use of gas allows for a smaller footprint than conventional oil-immersed transformers, while still providing excellent electrical insulation. However, SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas, and efforts are being made to reduce its use or to find alternative gases with similar insulating properties but with less environmental impact.
Another gas being explored is nitrogen. Nitrogen is an inert gas and is environmentally friendly. Although it does not have the same dielectric strength as SF6, it can be used in combination with other transformer insulation materials or in specific applications where voltage requirements are not extremely high and environmental factors are critical. Pole mounted transformer parts must include transformer insulation
Hybrid Insulation Systems: Meeting modern demands
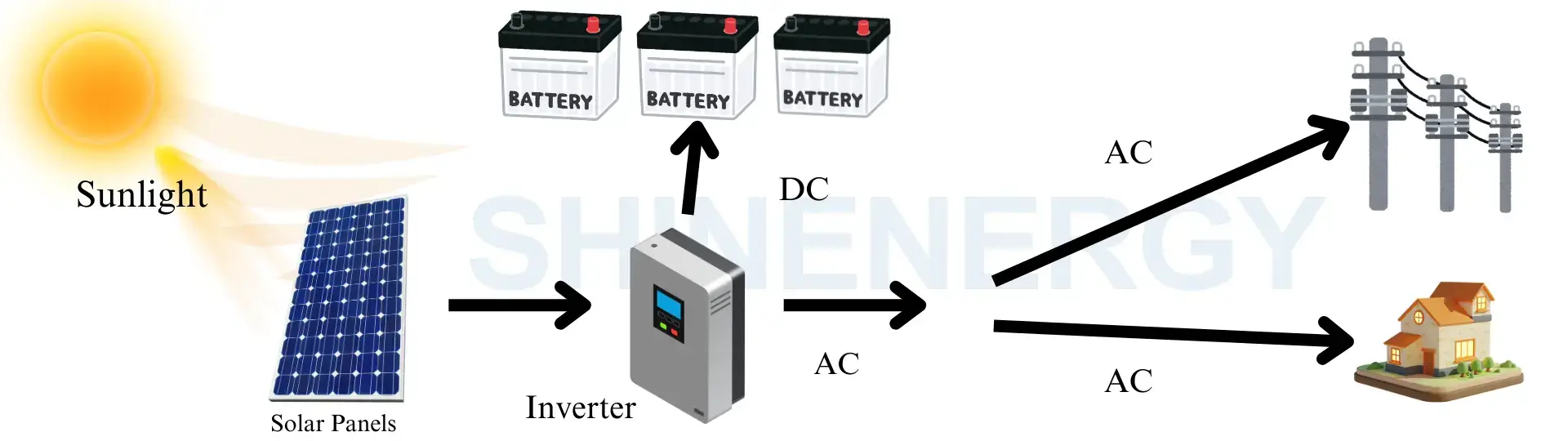
Figure 2 hybrid home solar system diagram
There are different kinds of transformers for various applications. Hybrid insulation systems combine different types of insulation to take advantage of their respective strengths. For example, a transformer may use solid insulation such as mica insulation tape for transformer around the windings, while employing oil as liquid insulation for cooling and to provide additional electrical insulation. In some cases, a small amount of gas insulation may also be introduced in specific areas to enhance overall performance.
These hybrid systems (hybrid home solar system diagrame) are designed to meet the needs of modern transformers operating under a wide range of conditions. They provide better thermal management, superior electrical insulation and increased durability compared to the use of a single type of insulation. For example, transformers installed in areas with variable ambient temperatures and high humidity, hybrid insulation systems are better adapted to these environmental challenges, ensuring reliable long-term operation.
Innovations in Transformer Insulation Materials

Figure 3 biodegradable oil
Eco friendly materials (e.g., biodegradable hydraulic oil)
The development of biodegradable hydraulic oil is a major innovation in the field of transformer insulation. Conventional mineral oils are petroleum-based and can pollute the environment in the event of a spillage. biodegradable hydraulic oil, like those derived from plants such as rapeseed or soya, offer a more sustainable alternative. These oils have similar electrical insulating properties to mineral oil and are able to break down on their own in the natural environment 0nt in the event of a spillage.
For example, in rural areas where some transformers are located in close proximity to agricultural land or bodies of water, the use of biodegradable hydraulic oil reduces the risk of contaminating the soil or water in the event of an biodegradable hydraulic oil. In addition, these oils are often produced using renewable resources, which is in line with the global trend to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote green energy infrastructure.
High-temperature and high-durability options
As transformers operate under increasingly demanding conditions, insulating materials are needed that can withstand high temperatures and have long-term durability. New ceramic-based materials are being developed that maintain their electrical and mechanical properties even at high temperatures. These materials can be used in the form of coatings or as part of composite insulation structures.
For example, in transformers used in industrial processes with high ambient temperatures due to the presence of heat sources such as furnaces in the vicinity, high-temperature-resistant insulation ensures that the transformer can continue to operate safely and efficiently without premature ageing of the insulation. This not only extends the service life of the transformer, but also saves the operator money by reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement.
Trends in lightweight insulation materials and sustainable insulation materials
Lightweight insulation is becoming increasingly important, especially in application scenarios where transformer weight is a requirement, such as mobile substation, or in installation environments with limited structural support. Composite materials made from glass fibre and polymer resin are being explored for this application. These materials provide good electrical insulation properties while being much lighter than conventional solid insulating materials such as oil-filled metal casings.
In addition, these insulating materials are being produced using sustainable manufacturing processes. For example, the use of recycled materials in the production of composite insulating materials or the reduction of energy consumption in the manufacturing process helps to make the entire insulation system more environmentally friendly, in line with modern sustainability goals.
4. Design Challenges in Transformer Insulation
Balancing thermal, mechanical, and dielectric requirements
Transformer insulation design must strike a delicate balance between thermal, mechanical and dielectric aspects. From a thermal point of view, the insulation material must be able to withstand the heat generated during operation without degradation. askarel-insulated transformers requires the selection of materials with suitable thermal conductivity and heat resistance. For example, if the insulating material is not able to dissipate heat efficiently, this can lead to overheating of the windings, which in turn shortens the life of the transformer and increases the risk of insulation failure.
From a mechanical point of view, the insulation needs to be able to withstand the forces applied to it during transport, installation and normal operation. Windings can vibrate due to electromagnetic forces, and the insulation must be able to maintain its shape and integrity under these mechanical stresses. From a dielectric point of view, askarel insulated transformer must have sufficient dielectric strength to withstand the applied voltage. If this balance is not achieved, for example by selecting a material with good dielectric properties but poor thermal conductivity, the transformer may be exposed to performance problems and a potential risk of failure.
Solutions for aging and environmental stressors
Insulation deterioration is a major issue as transformers need to operate for many years. Exposure to factors such as moisture, oxygen, and temperature changes degrade the insulation over time. To combat the problem of aging, Shinenergy has adopted encapsulation techniques using materials. Which are more resistant to these environmental stress factors. For example, solid insulating materials are coated with moisture-resistant coatings, or sealed designs are used in transformers to prevent the ingress of moisture and oxygen.
In environments with high levels of pollution or the presence of corrosive substances. Special insulation materials or protective coatings are used. In coastal areas, where transformers are exposed to salt-laden air, the use of corrosion-resistant coatings on the outer surfaces of insulating materials and the selection of materials less affected by salt corrosion help to extend the service life of the transformer and maintain its insulation integrity.
5. Maintenance and Longevity of Insulation Systems
Diagnostic tools (e.g., DGA, partial discharge testing)
Diagnostic tools play a vital role in assessing the condition of transformer insulation. Dissolved gas analysis (DGA) is a commonly used technique to detect early signs of internal faults, such as overheating or electrical discharges, by analyzing gases dissolved in transformer oil. For example, if the concentration of certain gases such as hydrogen, methane or ethylene is elevated in the oil. This could mean that there is a problem with the insulation of the transformer or that there are hot spots within.
Partial discharge testing is another important diagnostic method that can detect small electrical discharges. Which may be occurring within the insulation, identifying problems before these discharges develop into complete breakdowns. This is achieved by placing sensors around the transformer to measure the electrical signals associated with partial discharges. By performing these tests on a regular basis, maintenance personnel are able to detect potential problems as early as possible.It take corrective action to prevent further damage to the insulation, thereby extending the life of the transformer.
Preventative measures to extend lifespan
Preventive measures include maintaining proper operating conditions, which means ensuring that the transformer operates within its rated temperature and voltage range. Regular cleaning of the exterior of the transformer to remove dust and debris also helps to improve heat dissipation and reduce the risk of contamination of the insulation.We need to carefully check the insulating varnish for transformer winding of the transformer coil to ensure there are no short circuits or other faults.
Regular monitoring of oil levels and quality, and replenishing or replacing the oil as necessary, are essential operations. In addition, routine inspections of the transformer’s mechanical components, such as looking for loose connections or signs of vibration damage, help maintain the overall integrity of the insulation system. By implementing these preventative measures, the life of transformer insulation can be significantly extended, reducing the need for costly replacements and minimising downtime.
A comparative chart of materials and their applications
| Insulation Material | Application Scenarios | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Mineral Oil | Oil-immersed transformers in various environments | Good electrical insulation performance, effective coolant | Non-biodegradable, may cause environmental harm when leaked |
| Biodegradable Oils (such as ester oils) | Transformers in environmentally sensitive areas, some industrial application scenarios | Environmentally friendly, with good electrical properties | Thermal characteristics may be slightly different compared to mineral oil, and the cost may be higher in some cases |
| Cellulose Paper | Used in combination with oil in many transformers | Inexpensive, with good electrical insulation performance | Susceptible to moisture and aging |
| Mica Tape | Transformers in high-temperature and high-voltage application scenarios such as power plants | High thermal stability, excellent dielectric strength | Relatively expensive |
| Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) | High-voltage gas-insulated switchgear, some special transformers | High dielectric strength, enabling compact design | A potent greenhouse gas, with environmental issues |
6. Conclusion: Elevating Transformer Performance
Throughout our discussion of transformer insulation. We have seen the key role it plays in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of transformers. From different types of insulation, such as solid, liquid, gas and hybrid insulation systems, to innovative materials. Such as environmentally friendly oils and high-temperature-resistant materials, every aspect contributes to meeting the ever-evolving needs of modern power systems. Our company specializes in the field of transformer insulation and offers you excellent transformer insulation services . As well as comprehensive transformer insulation solutions thanks to a professional team and a wealth of experience.
7. FQA
What are the main applications and advantages of the Masonite dielectric vapor barrier in electrical equipment?
Applications:
Used in transformers and electrical cabinets to prevent water vapor from reaching internal components. It is like protecting transformer windings and electrical parts in cabinets from moisture damage.Antique glass transformer insulators of Bushing insulator for transformers
Advantages:
Good dielectric strength to avoid electrical short circuits.
Effectively resists moisture, extending equipment lifespan.
Durable and can withstand some wear and tear.
Compatible with other common electrical insulating material used in transformers for easy integration.
What is vintage transformer cloth insulation?
It’s the cloth insulation material used in old transformers to separate electrical currents and ensure safety. Transformers are usually rated in units called kilovolt-amperes.What are transformer windings typically wrapped around? The core.The insulation of transformer windings plays a crucial role in ensuring its safe operation.
What insulating materials do dry type transformer suppliers usually choose?
dry type transformer manufacturers
The development of advanced technology demands the combination of quality transformer and electronics to meet the increasing requirements for power stability. Top 10 power transformer manufacturers in usa.
how many types of transformers are there?
Autotransformers/Isolation Transformers/Step-up Transformers/Step-down Transformers
what are the different types of transformers insulation?
basic insulation level of transformer: The different types of transformers insulation.Which include Class A, Class E, Class B, Class F, Class H, and Class C.
what is inside of a transformer?
Inside a transformer, there are a core (usually made of ferromagnetic materials), windings (primary and secondary coils), insulation materials, and sometimes a tap changer, a cooling system (like oil or air cooling), and a tank (for oil-cooled ones).
how many types of transformer are there?
What is Oil transformer and types of them?
oil transformer types
oil filled transformer manufacturers
An oil transformer uses transformer oil for cooling and insulation. Types include:
Mineral Oil Transformers: Use petroleum-based mineral oil, widely used in general power systems.
Synthetic Oil Transformers: Use chemically engineered synthetic oils, applied where fire safety is important.
what is a dry type transformer insulation class?
Dry type transformer insulation classes mainly include Class B, Class F and Class H. These classes define the temperature tolerance and insulation performance of the transformer. They guide its application in different environments based on heat and electrical insulation requirements. cast coil transformers


Pingback: Understanding Insulation Breakdown in Power Transformers
Pingback: How to Select the Right Pad-Mounted Transformer? - Voltori Transformer | Powering Canada with Precision & Performance
Pingback: HILO789
Pingback: ขายฝาก