Step-up transformers and step-down transformers have attracted much attention due to their unique functions. So this article will introduce in detail the definition, working principle, application, advantages, and disadvantages of step-down vs step-up transformers to help readers fully understand their importance and practical applications.
What Are Step-Up And Step-Down Transformers?
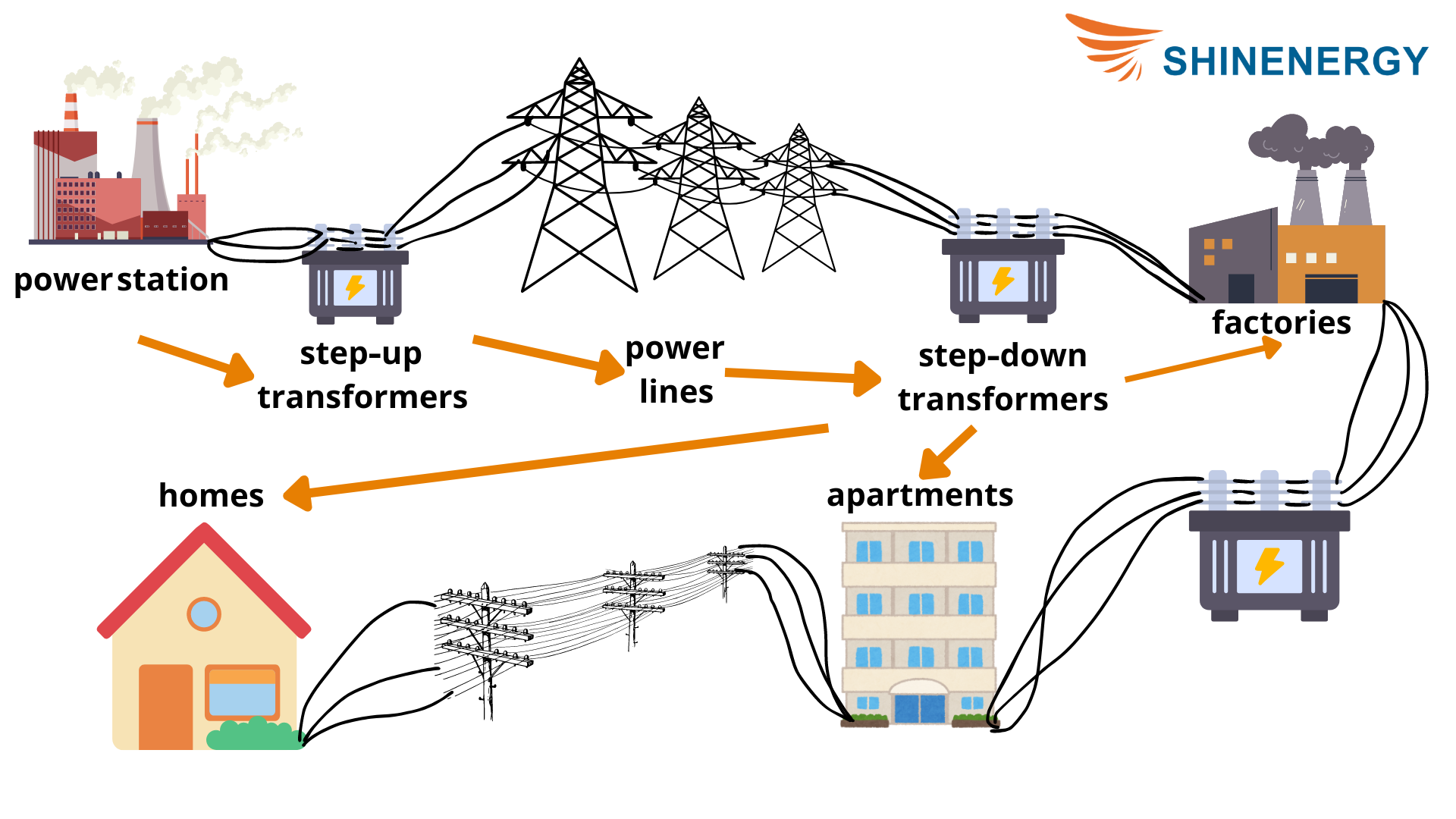
Figure 1-1 step up and step down transformer diagram
Today, transformers play a vital role in electrical systems in modern society. It can ensure efficient transmission of energy between circuits.
What Do Step-down Transformers Do?

Figure 1-2 step down transformers
It play a vital role in reducing high-voltage electricity to a lower, more usable voltage. This is necessary for safely powering household appliances, office equipment, and various electronic devices.
When electricity travels through power lines, it is typically at a very high voltage to minimize energy loss over long distances. However, this high voltage must be reduced before it reaches residential or commercial buildings.
Step-down transformers achieve this by lowering the voltage to a safer level, ensuring that electrical devices can operate correctly and safely.
What Does a Step-up Transformer Do?
Figure 1-3 step-up transformer
Step-up transformers are designed to increase the voltage of electricity from a lower level to a higher level. This process is essential in power generation and transmission systems.
For instance, electricity generated at power plants is typically at a lower voltage. To transmit this electricity efficiently over long distances, step-up transformers increase the voltage, which reduces the current and minimizes energy loss. By boosting the voltage, these transformers ensure that the electricity can travel over power lines with minimal loss, making the transmission process more efficient and cost-effective.
How Do Step-Up And Step-Down Transformers Work?
Understanding how step-up and step-down transformers work can help you appreciate their importance in everyday applications.
How does a step-up transformer work?
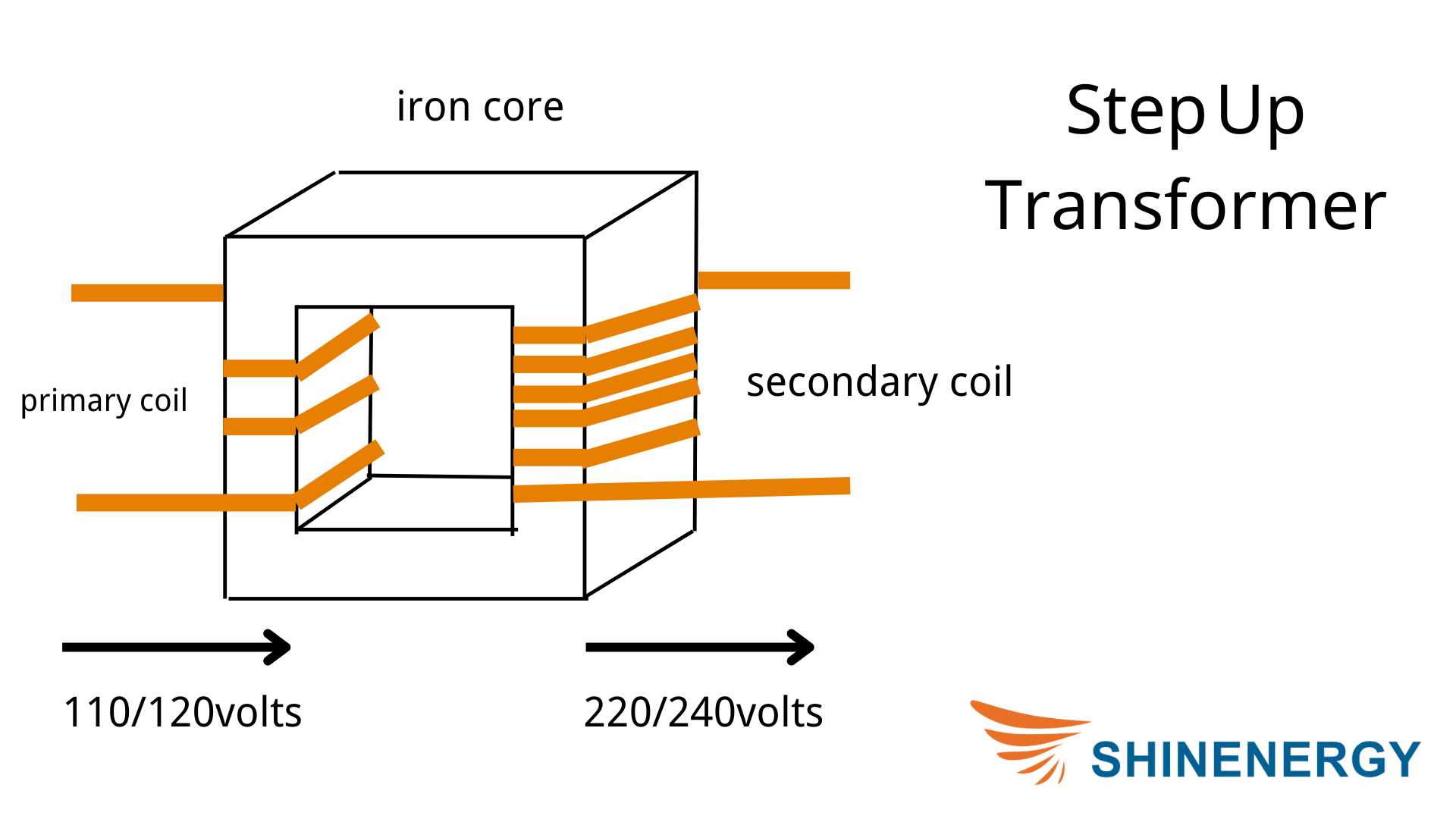
Figure 2-1 step-up transformer diagram
A step-up transformer increases the voltage from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
Input Current:
Alternating current (AC) flows into the primary coil.
Magnetic Field Creation:
The AC in the primary coil generates a magnetic field in the transformer’s core.
Electromagnetic Induction:
This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil.
Voltage Increase:
Because the secondary coil has more turns of wire than the primary coil, the induced voltage is higher. This increased voltage allows for efficient long-distance power transmission by reducing energy loss.
How Do Step-down Transformers Work?
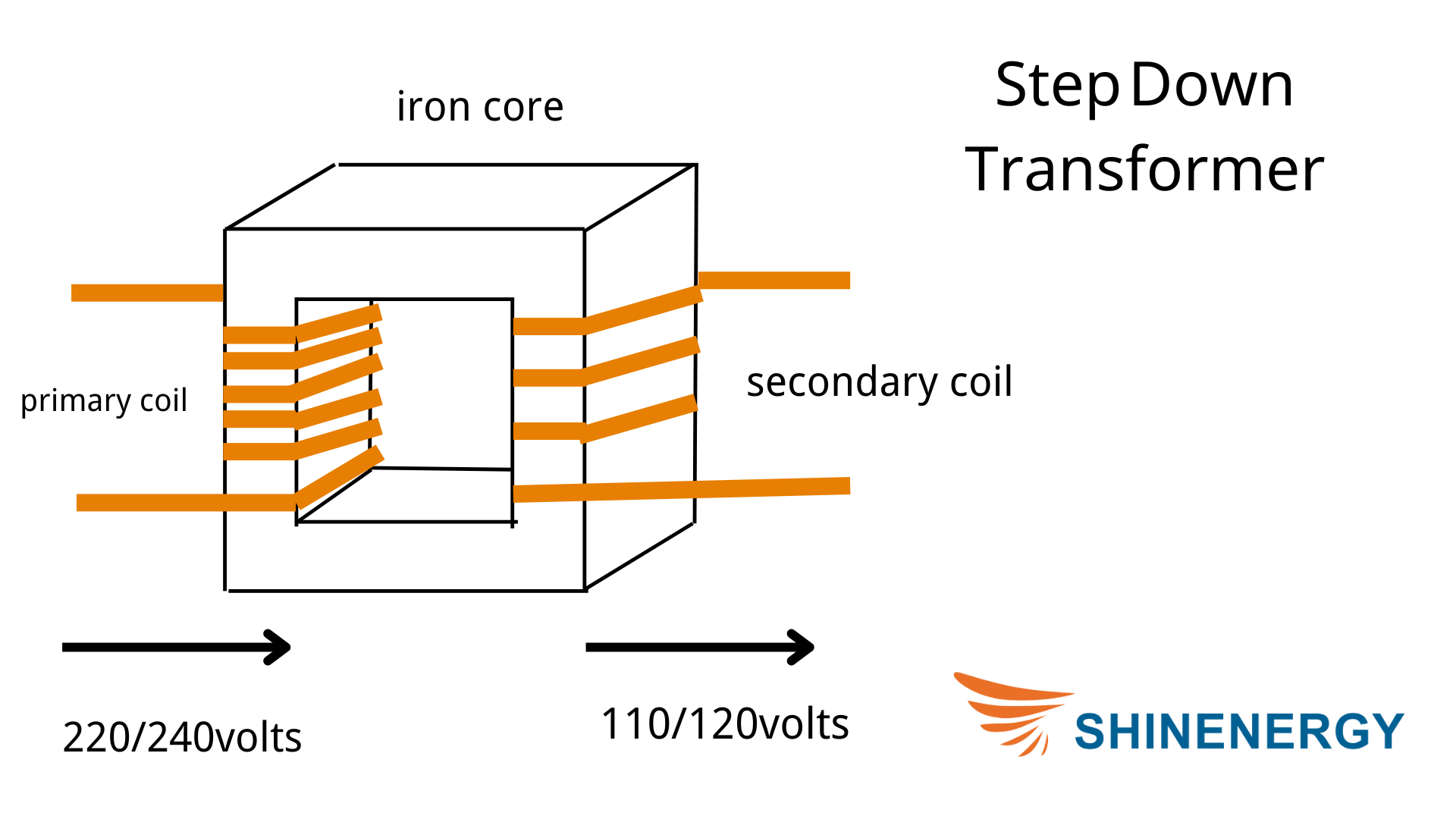
Figure 2-2 step-down transformer diagram
Step-down transformers decrease the voltage from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
Input Current:
An alternating current (AC) enters the primary coil.
Magnetic Field Creation:
The AC in the primary coil generates a magnetic field in the transformer’s core.
Electromagnetic Induction:
This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil.
Voltage Decrease:
The secondary coil has fewer turns of wire than the primary coil, resulting in a lower induced voltage. This decreased voltage is suitable for powering household appliances and electronic devices safely.
Applications Of Step-Up And Step-Down Transformers
Step-up and step-down transformers are integral to various aspects of our daily lives and industrial processes such as step-up and step-down transformers’ national grid. Here’s a look at where and how these transformers are used:
Applications Of Step-Up Transformers
Step-up transformers are primarily used in power generation and transmission systems.

Figure 3-1 Applications of Step-Up Transformers of Power Plants
At power generation stations, electricity is produced at relatively low voltages. Step-up transformers increase this voltage to extremely high levels, facilitating the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. By reducing current, energy losses due to resistance in the transmission lines are minimized. generator step-up transformer

Figure 3-2 Applications of Step-Up Transformers of Renewable Energy Systems
In solar and wind power systems, the generated electricity often needs to be converted to a higher voltage to be fed into the grid. Step-up transformers are crucial in this process, ensuring that the renewable energy generated can be efficiently integrated into the existing power infrastructure.
Industrial Applications:

Figure 3-3 Applications of Step-Up Transformers of Industrial Applications
Certain industrial processes and equipment require high voltages to operate effectively. Step-up transformers provide the necessary voltage levels to power heavy machinery, manufacturing equipment, and other high-voltage industrial tools.
Common Examples:
step-up transformer 110v to 220v,120v to 240v step-up transformer,step-up transformer 110v to 240v,step-up transformer 208 to 480,step-up transformer 240 to 480
Applications Of Step-Down Transformers
Step-down transformers are vital in making high-voltage electricity usable every day.

Figure 3-4 Applications of Step-Down Transformers of Residential Areas
Electricity transmitted through high-voltage power lines needs to be reduced to a safer level before it can enter homes. Therefore, step-down transformers play a crucial role in this process, ensuring that the high-voltage electricity is converted to a level that is safe for household use. Step-down transformers lower the voltage to suitable levels, ensuring that household appliances and electronic devices operate safely.

Figure 3-5 Applications of Step-Down Transformers of Commercial Buildings
Similar to residential applications, commercial buildings rely on step-down transformers to convert high-voltage electricity from power lines into lower voltages that can be safely used for lighting, HVAC systems, and office equipment.
Electronic Devices:

Figure 3-6 Applications of Step-Down Transformers of Electronic Devices
Many electronic devices require specific low-voltage inputs to function correctly. Step-down transformers in power adapters and chargers reduce the voltage from standard outlets to the required levels for devices like laptops, smartphones, and other gadgets.

Figure 3-7 Applications of Step-Down Transformers of Distribution Networks
After electricity is transmitted over long distances at high voltages, it passes through a series of step-down transformers at substations and distribution points. These transformers progressively lower the voltage to levels appropriate for final delivery to consumers.
Common Examples:
step down transformers 240v to110v
step down transformer 480 to 120
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Step-Up And Step-Down Transformers
Advantages Of Step-Up Transformers

Figure 4-1
Efficient Power Transmission:
By increasing the voltage, step-up transformers reduce the current, which minimizes energy loss during long-distance transmission. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining a stable power supply over vast distances.
Reduced Transmission Costs:
Higher voltage levels mean lower current, which in turn reduces the size and cost of transmission lines and related infrastructure. This makes the overall power distribution system more economical.
Support for Renewable Energy:
Step-up transformers are essential in integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid. They enable the transmission of electricity generated at low voltages to higher voltages needed for grid compatibility.
Disadvantages Of Step-Up Transformers

Figure 4-2
Increased Electrical Hazard:
Higher voltages pose greater safety risks, requiring stringent safety measures and equipment to protect personnel and infrastructure from potential electrical hazards.
Complexity and Cost:
The design and construction of step-up transformers can be complex and expensive, especially for high-capacity units. This can increase the initial investment required for power transmission systems.
Maintenance Requirements:
High-voltage transformers require regular maintenance to ensure reliability and prevent failures, which can add to operational costs.
Advantages Of Step-Down Transformers

Figure 4-3
Safe Voltage Levels:
Step-down transformers reduce high-voltage electricity to safer levels suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial use. This ensures the safety of electrical devices and prevents electrical hazards.
Versatility:
They are used in a wide range of applications, from household electronics to large-scale industrial equipment. This versatility makes them essential in everyday electrical systems.
Improved Device Longevity:
By providing the appropriate voltage levels, It helps prevent damage to electrical devices, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing replacement costs.
Disadvantages Of Step-Down Transformers

Figure 4-4
Energy Loss:
Despite their efficiency, It can still experience energy losses during the voltage conversion process. And These losses, although minimal, can accumulate over time and impact overall efficiency.
Size and Weight:
For high-power applications, It can be large and heavy, making installation and maintenance more challenging.
Initial Cost:
While generally more affordable than step-up transformers, high-quality step-down transformers can still represent a significant initial investment, especially for large-scale applications.
Conclusion

Figure 5-1
Understanding the functions and applications of step-up and step-down transformers is crucial for anyone involved in electrical systems. These transformers are essential for managing voltage levels, and ensuring the efficient and safe operation of various electrical devices and systems. By increasing or decreasing voltage as needed, It plays a vital role in our daily lives, from powering household appliances to enabling long-distance power transmission.
FAQs
What Is The Main Difference Between Step-up And Step-down Transformers?
Step-up transformers increase voltage while decreasing current, whereas step-down transformers decrease voltage while increasing current.
How Do Transformers Reduce Energy Loss In Power Transmission?
Do step-down transformers waste electricity? Many people have this question. While step-up transformers minimize energy loss by increasing voltage and decreasing current, step-down transformers operate differently. They reduce high voltage to safer levels for use.
What Are The Safety Considerations When Using Transformers?
Are step-down transformers safe? Proper insulation, regular maintenance, and ensuring that the transformers are used within their specified voltage and current limits are essential for safe operation.
Why Are Step-down Transformers Used?
Step-down transformers are used to reduce high voltage levels to safer, more manageable levels. This is crucial for several reasons.
high-voltage electricity from power lines needs to be lowered to safe levels for household and commercial use. Without step-down transformers, electrical appliances and devices could be damaged or pose safety risks.
What Is The Step-Down Transformer Formula?
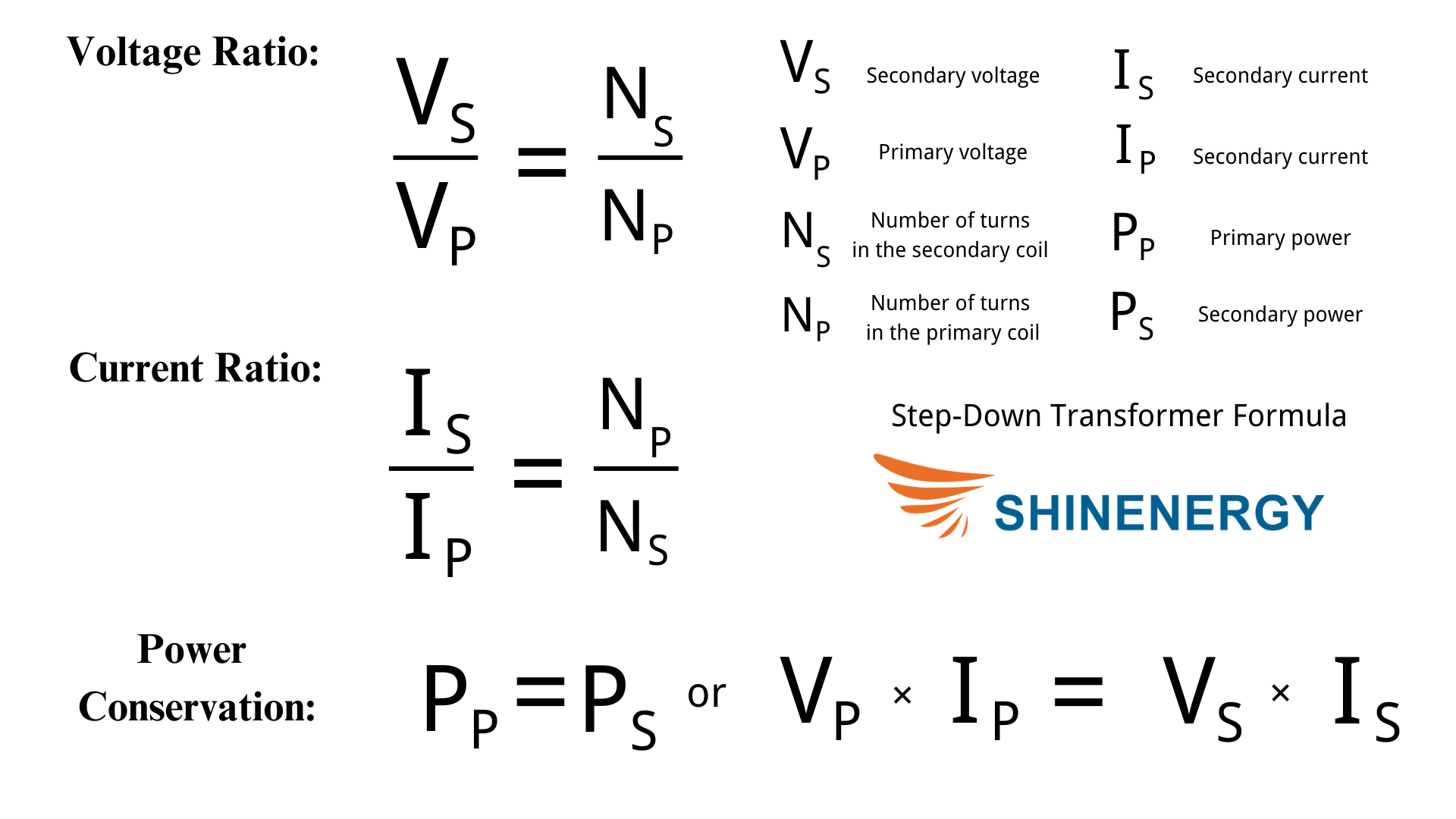
Figure 7-1 the Step-Down Transformer Formula
What Is The Step-Up Transformer Formula?
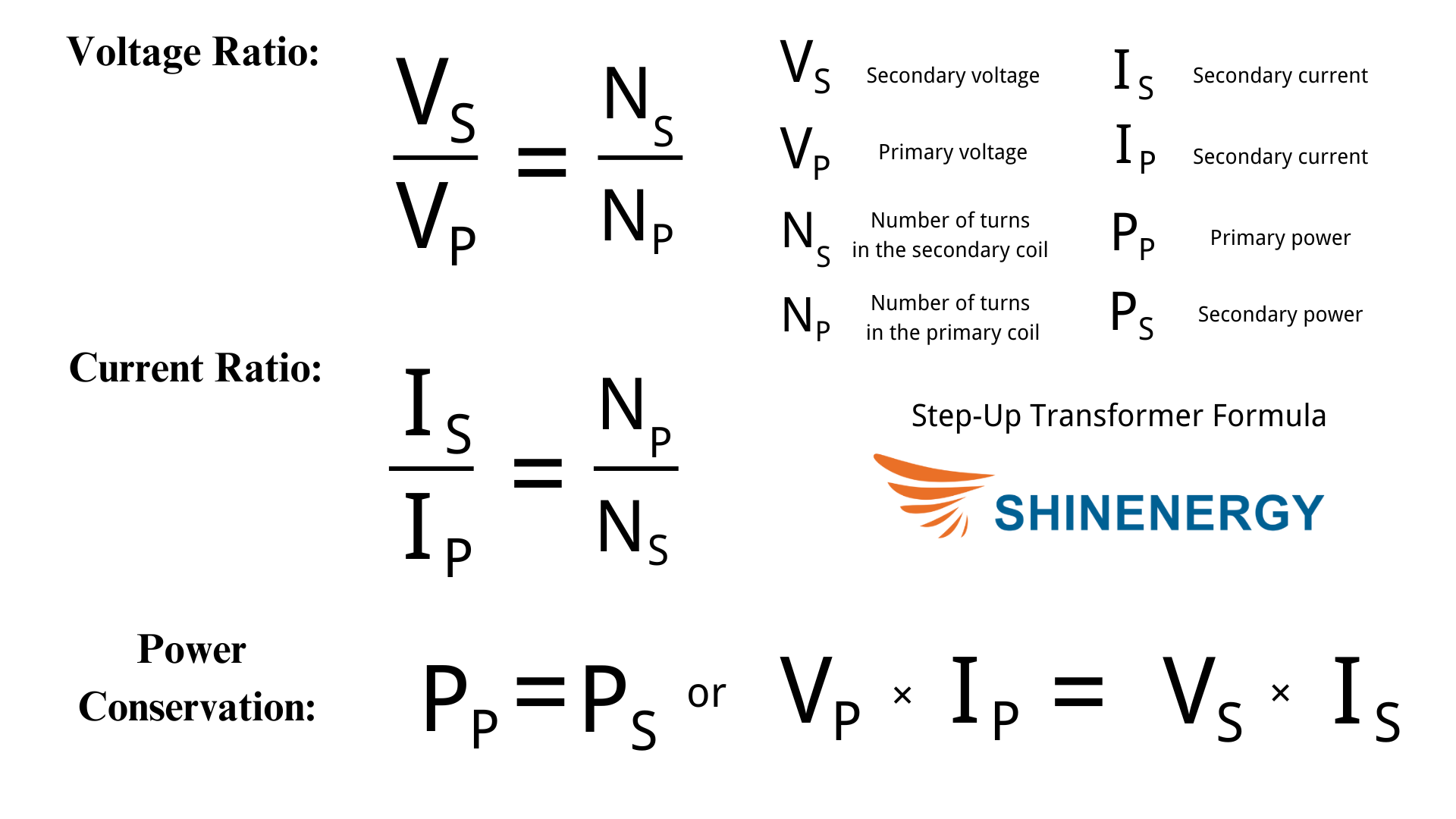
Figure 7-2 the Step-Up Transformer Formula
What are the classifications of transformers?
What is an isolation transformer?


Pingback: https://sultangejmskazino365.top/
Pingback: altogel