
In modern power systems, transformers play a crucial role in ensuring a stable supply of electricity by transmitting power from the power station to the user side through high voltage. In the whole power transmission process, the live wire dc, Neutral line and Earth is an indispensable key component, they work together to ensure the normal operation of the power system and the user’s electricity safety.
In this article, we will introduce the functions of Live Earth and Neutral Wire in detail, and through comparative analysis, help readers clearly understand the difference between them, and their key role in the transformer system.
Figure 1 Live wire vs ground wire vs neutral wire
Definition and Function of live vs neutral vs ground wire
Figure 2 ground earth and neutral
Definition and Function of live wire: what is live wire meaning?
Figure 2-1 Meaning of live wire
What is a live wire? live wire, also known as phase or ribbon wire, is the conductor in an electrical system that carries the current and delivers it to the equipment. It is the most critical component of the power supply line and is directly responsible for transferring power from the transformer to the loads and ensuring that electrical equipment can function properly. Typically, the live wire carries a high voltage, so contact with the live wire in an electrical system requires special care to avoid the risk of electric shock. In DC circuits, the live wire electric carries current just as in AC systems, but understanding the role of a DC live wire in electric systems is crucial for proper wiring and safety.
What is neutral line and what does a neutral wire do?

Figure 2-2 What is a neutral wire
what is the neutral? The wire neutral is the return line in an electrical system that brings current from the electrical equipment back to the transformer or distribution box, completing the loop closure of the current.

Figure 2-3 What wire is neutral?
What does the neutral wire do? Although the neutral wire is usually voltage free, it may carry some voltage in an unbalanced circuit. The primary function of the neutral wire is the neutral wire a ground to help balance the voltage so that the circuit can operate in a stable manner.
Definition and Function of Earth Wire
Figure 2-4 Which wire is ground
The earth wire serves as a protective wire in the power system, directing excess or fault current from the electrical equipment casing into the difference between neutral wire and earth wire through the grounding device. This prevents the equipment casing from becoming electrified and helps avoid electrocution accidents. Earth wires usually do not carry current during normal operation and only function during electrical faults. When the ground wire activates, it lights up your life.When ground wire lites up your lite.
The role of Live Earth and Neutral Wires for Transformers
Figure 3 Live neutral and earth wire
Effect of live wire on transformer current transfer process
In a transformer system, the live wire high voltage wiring is connected from the output of the transformer to the power-using device to deliver current to the target device. In single-phase circuits, the live wire and earthing colour wire work together to accomplish power transmission and loop closure; in three-phase circuits, the three live and bare wire work in concert to provide more efficient power transmission.
The role of the neutral wire in a transformer
In a transformer system,which wire is neutral is usually connected to the neutral point of the transformer. In single-phase circuits, the neutral wire, along with what are live wires, makes up the complete circuit, ensures the smooth transmission of power between equipment, and helps keep the voltage balanced. In three-phase circuits, the neutral wire colour is used to maintain phase balance and reduce voltage fluctuations in equipment operation.
Ground protection in transformers requires a ground wire
In a transformer system, difference between neutral and earth conductor is connected to the transformer’s enclosure or neutral point to ensure that any leakage currents due to faults or unforeseen circumstances can be safely introduced into the ground vs neutral wire via the earth conductor. This feature is vital to protect electrical equipment and users from the risk of electric shock, especially in the event of short circuits, overloads and other problems with the equipment or wiring, and the ground vs neutral wire is effective in preventing danger from occurring.
Live Earth and Neutral Wire Considerations

Figure 4 Live Wire vs neutral wire vs ground wire
Safety Risks and Precautions for Live Wire
The Importance of Neutral Wire for Load Balancing
What is neutral wire?Another key role of the live neutral earth wire in an electrical system is to help balance loads. In the case of large single-phase loads. What does neutral wire do? the live neutral ground wire maintains a smooth loop of current, preventing current backflow or equipment damage. If the load is unbalanced, the Neutral line will carry some of the current, so its safe design is equally important.
Ground wire prevents electric shock and equipment damage
Live Earth and Neutral Wires: the difference between ground and neutral and earth
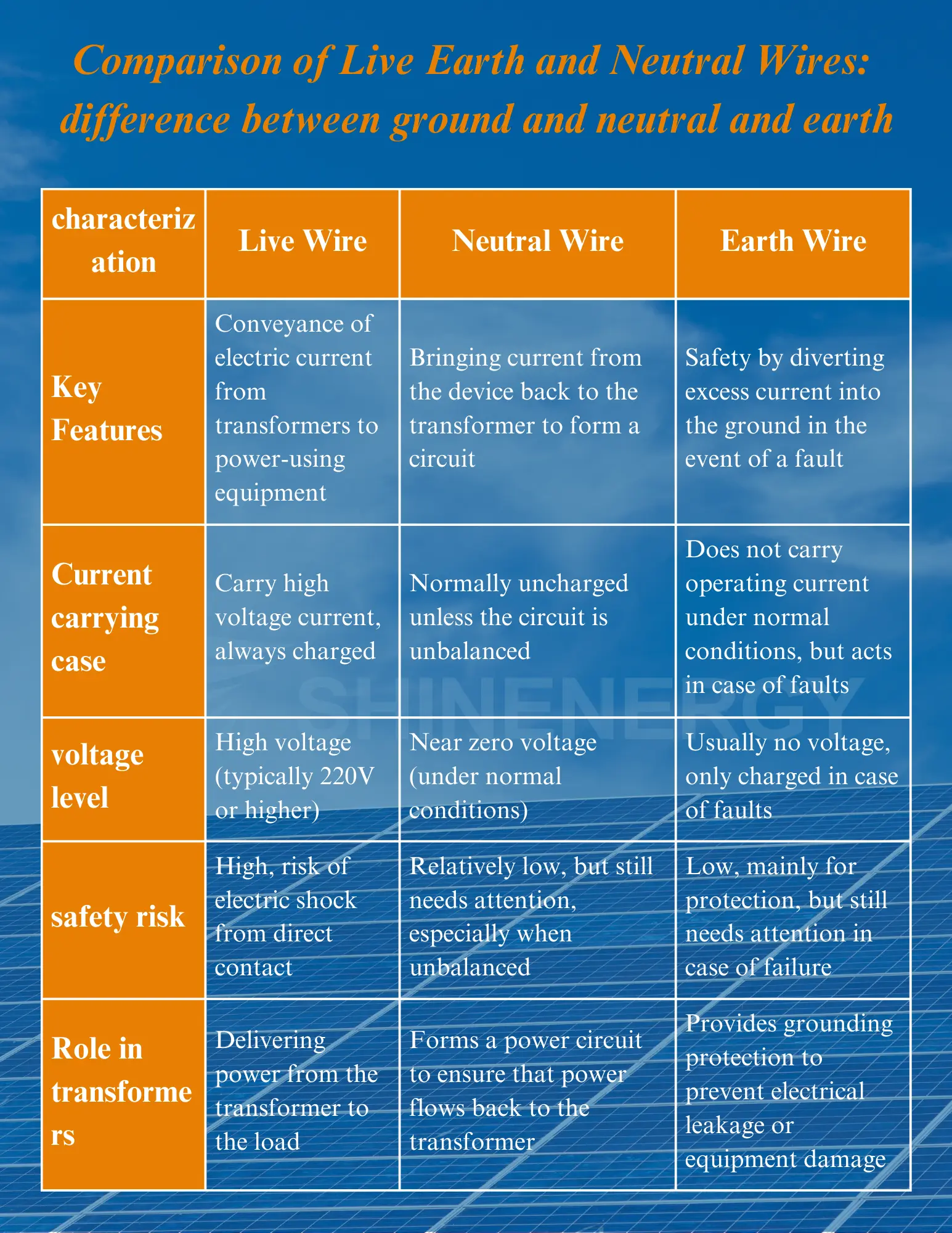
Figure 5 difference between neutral and ground
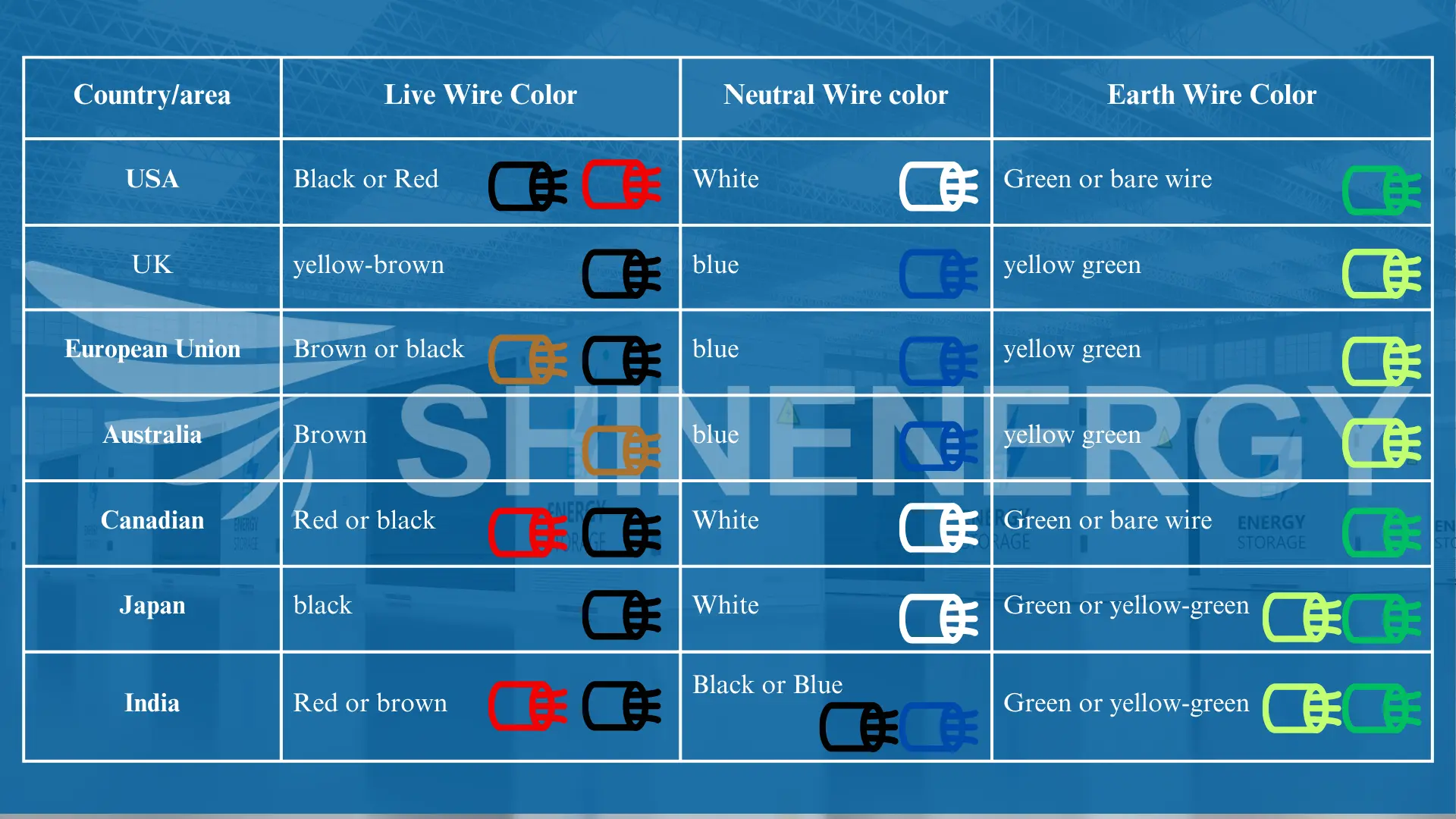
Figure 5-2 live earth neutral colours/line ground neutral colors
- What colour wire is earth?
Colours of earth neutral and live:The earth wire is typically green or yellow-greenin most countries. - What colour is earth wire?
Live neutral ground colors:The earth wire is generally green or yellow-green, depending on the country. - What color is the earth wire?
Earth live neutral wire: The earth wire is usually green or yellow-green in most places. - What is the color of earth wire?
Earth live and neutral wires:The earth wire’s color is typically green or yellow-green.
Summarize the live earth and neutral wires
Figure 6 live neutral protect earth
Live Wire, Neutral Wire and Earth Wires are key components of an electrical system and each performs an important task: definition of live wire is responsible for transmitting power from the transformer to the equipment, line load neutral Wire is neutral wire same as ground, and Earth Wire provides security for the electrical system.
FAQ
Is there a connection between positive and negative wires and fire and zero ground wires?
What is the difference between hot wire and load wire?
What is the diferent between hot wire and load wire?The hot wire carries electrical current from the power source to the switch or electrical device. The load wire refers to the wire that carries current from the switch to the device or appliance.
How to identify neutral wire?
What a neutral wire does?The purpose of neutral wire is often identified by its color, which is usually blue in the UK and EU, or white in the US. In some cases, a multimeter can be used to test for the neutral to ground wire by checking for voltage differences between the wires.
How to identify a neutral wire?
To identify a live neutral wire colours, look for a wire that is typically white (US) or blue (EU/UK) in color. You can also use a voltage tester or multimeter to check that it has close to zero voltage when compared to light with no ground wire.
What is the neutral wire for in electricity?
The difference between earthing and neutral wire completes the electrical circuit by returning current back to the power source. It helps balance the voltage in the circuit and ensures a stable flow of electricity.
What is the difference between neutral and ground?
Difference between earthing and grounding and neutral.The electrical neutral wire is part of the electrical circuit, carrying current back to the source, while the electrical ground wire purpose is a safety feature that directs excess current safely into the earth in case of a fault or electrical surge.
What is the difference between a neutral and a ground?
The electrical neutral vs ground carries current under normal operation, while the light with no ground wire only carries current in the event of a fault to prevent electric shock by grounding excess current.
Does the neutral wire carry current?
Yes, what is neutral wiring?the neutral wire carries current in a balanced circuit, returning the current to the power source after it has passed through the load.
How to find neutral wire?
Which wire is the neutral wire?Difference between grounding and neutral .To find the earthed neutral wire, check the color coding (usually white in the US or blue in the UK/EU). You can also use a voltage tester to confirm that what is the purpose of a neutral wire the neutral line electricity wire shows little to no voltage compared to the live or hot wire.
what is the function of a ground wire?
what is the purpose of a neutral conductor?
what is the color of live wire?
what colour of wire is live
colour of live and neutral wires



Pingback: nomad cosino
Pingback: 123bet login
Pingback: รับงานเอง
Pingback: หาแม่บ้าน