In our daily lives, we simply press a switch, and the lights come on instantly, with electrical appliances running smoothly. The single phase vs 3 phase power seems that the power supply is an ordinary thing. However, have you ever wondered what the fundamental differences are between the stable power at home and the powerful energy source in factories? When we talk about “Single Phase vs Three Phase Power”, it’s not just a collision of two technical terms but a profound exploration of energy distribution, efficiency, and application scenarios.
From the small lamp that illuminates your bedroom to the powerful force that drives large machinery, single phase versus three phase power are playing crucial roles in every corner of our lives in completely different ways. Now, let’s uncover their mysterious veils together and delve deep into the mysteries between them.

Figure 1-1 Single Phase vs Three Phase
Single Phase vs Three Phase: Defining Single Phase and Three Phase Power Systems
What is Single Phase Power?
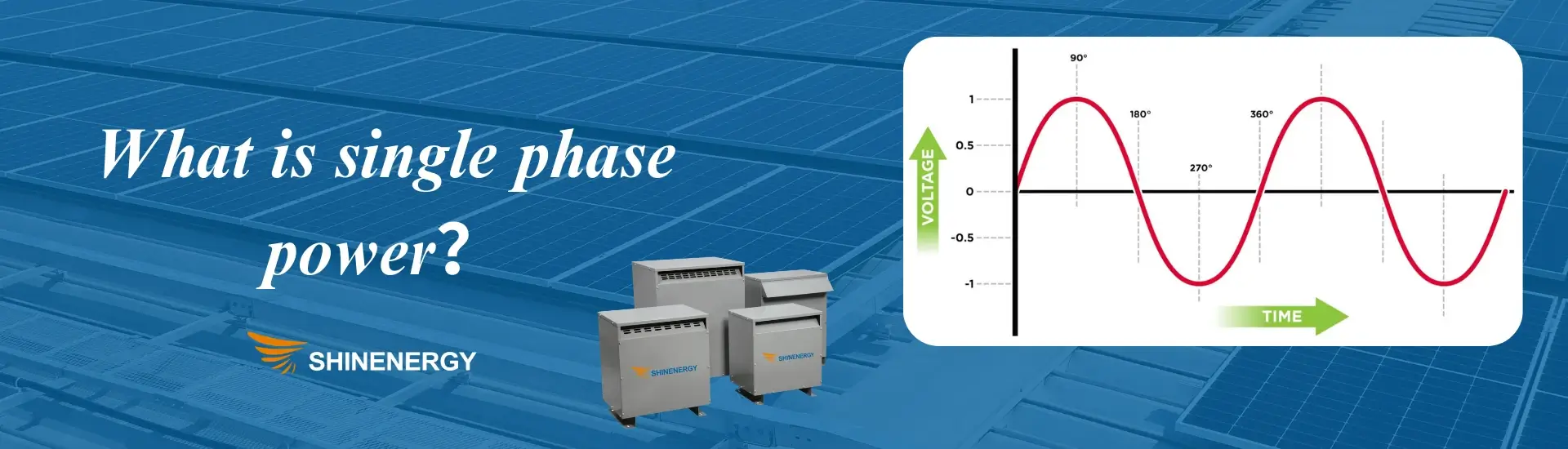
Figure 1-2 3 phase vs single phase power: what is single phase
Single phase power is an alternating current (AC) system that delivers electricity using a single sinusoidal voltage waveform. single phase electrical wiring operates with one live (hot) wire and one neutral wire, sometimes accompanied by a ground wire for safety. The voltage of single phase alternates periodically, creating a pulsating power flow.
This type of power is commonly used in residential homes, small businesses, and low power applications due to its simplicity and cost effectiveness. However, it is less efficient for high power loads compared to three phase ac supply.
What is three phase power?

Figure 1-3 1 phase vs 3 phase power: what is 3 phase electricity
What is 3 phase power? The 3 phase electric is an AC 3 phase system with three voltage waveforms. Each waveform is 120 degrees apart. The three phase electric power uses three live wires and sometimes a neutral wire.
This system provides stable and continuous power. The three phases of power reduces voltage drops and power loss. The three phase electrical works well for industrial machines, large motors, renewable energy, and data centers.
Three Phase vs Single Phase Electricity:
Exploring the Structure of Single Phase and Three Phase voltage Systems

Figure 2-1 three phase to single phase: 3 phase to single phase
what is single phase power Structure?

Figure 2-2 three phase to one phase transformer: 3 phase electric
A single electric phase system typically consists of a live (hot) wire and a neutral wire. Some systems also include a ground wire for additional safety. The voltage alternates between positive and negative peaks, resulting in a pulsating power supply.
what is three phase electricity Structure?
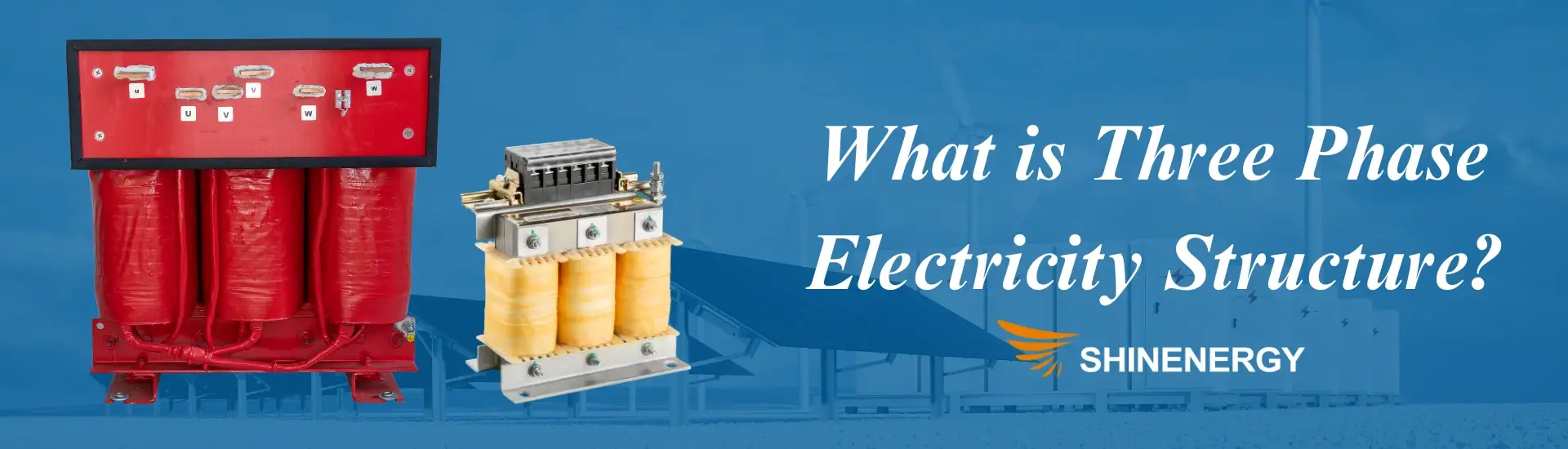
Figure 2-3 three phase vs single phase: three phase electric
how three phase electricity works? A three phase electric power system comprises three live wires (or electrical phases) and, in most cases, a neutral wire. The voltage of three phases deliver power in a rotating sequence, ensuring a smoother and more consistent energy flow. This results in higher power efficiency and the ability to handle larger loads.
Single Phase vs Three Phase electricity:What is difference between single phase and three phase electricity?

Figure 3-1 difference between single phase and 3 phase power supply
single phase vs 3 phase electricity explained:Advantages of Single Phase Power
Single phase power has a simple structure and low cost. It uses only one live wire and one neutral wire, making installation easy. It works well for homes, small businesses, and offices. Most household appliances, like lights, fans, and TVs, run smoothly on single phase power. It is widely available and meets the needs of low power applications.

Figure 3-2 difference between single phase and three phase supply
single vs 3 phase:Disadvantages of Single Phase Power
Single phase power has limited capacity and is not suitable for heavy loads. three phase power Voltage fluctuates more, which can affect sensitive equipment. Power delivery is not continuous, leading to lower efficiency. It loses more energy over long distances. Large motors and industrial machines do not perform well with single phase power.

Figure 3-3 difference between single and three phase electricity
Electrical 3 phase vs single phase:Advantages of Three Phase Power
The power three phase provides stable and efficient energy delivery. The 3 phase electricity handles heavy loads with less voltage fluctuation. Motors run smoothly and last longer. The 3 phase electrical wiring reduces energy loss over long distances. This 3 phase electrical system works well for industrial machines, data centers, and large scale power applications.

Figure 3-4 difference between 3 phase and single phase supply
one phase vs 3 phase electric power:Disadvantages of Three Phase Power
3 phase electrical power costs more to install and maintain. It requires complex wiring with three live wires, making setup harder. Small homes and businesses do not need this three phase power system since it is designed for heavy loads. Maintenance is more demanding and requires skilled professionals.

Figure 3-5 difference between single phase and three phase electricity explained
Identifying the Ideal Applications for Single Phase and Three Phase Power
Single Phase versus Three Phase Power:Single Phase Applications
single phase electric power is widely used in homes, small businesses, and offices. 1 phase electricity t powers household appliances like lights, fans, TVs, and kitchen devices. Many electronic devices, including computers and printers, run on single phase power. HVAC systems, such as air conditioners and heaters, also rely on it. This system is common in indoor and outdoor lighting, making it essential for daily life.
Figure 4-1 phase from single phase transformer
1 Phase vs 3 Phase Power Explained: Three Phase Applications
Three phase power is used in industrial facilities, large businesses, and high power applications. three phase electrical power runs heavy machinery, large motors, and manufacturing equipment efficiently. Data centers rely on it for stable power supply and cooling systems. Renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar farms, use three phase electric power for energy conversion. Rail transportation and electric vehicle charging stations depend on it for reliable performance. This system is ideal for applications that require high power and continuous operation.

Figure 4-2 single vs three phase
Understanding the Role of one phase vs three phase in Electrical Components
Single Phase Transformers vs Three Phase Transformers

Figure 5-1 Single Phase Transformers vs Three Phase Transformers
Single phase transformers work with single phase power systems. They step up or step down voltage for homes, small businesses, and low power applications. These transformers are simple, cost effective, and easy to install. However, they are less efficient for large loads and industrial use.
Three phase transformers handle three phase power. They provide stable voltage for industrial plants, data centers, and power grids. These transformers support heavy machinery, large motors, and renewable energy systems. They are more efficient and reduce energy loss over long distances. However, they cost more and require complex installation.
Difference between Single Phase Transformers vs Three Phase Transformers

Figure 5-2 single phase vs three phase transformer
| Feature | Single Phase Transformer | Three Phase Transformer |
| Power Source | Works with single phase power | Works with three phase power |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for heavy loads | More efficient for high power applications |
| Applications | Homes, small businesses, lighting systems | Industrial plants, data centers, power grids |
| Installation | Simple and easy to install | More complex 3 phase ac wiring and setup |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for small scale use | Higher cost, designed for heavy loads |
| Load Handling | Supports light to moderate loads | Handles high power and continuous loads |
| Voltage Stability | More fluctuations, less stable | More stable and balanced power supply |
| Energy Loss | Higher energy loss over long distances | Lower energy loss, better for long distance transmission |
| Core Structure | EI core or C core, simple design | Three leg or five leg core, better magnetic balance |
Difference between Single Phase Reactors vs Three Phase Reactors
Single phase reactors are suitable for small power conditioning and household equipment. They are simple in structure, easy to install and low in cost, but they are inefficient, have high losses and are difficult to withstand high power loads. In contrast, three phase reactors are more suitable for industrial applications such as motor drives and harmonic filtering. They can provide more stable voltage and higher efficiency, support high power and continuous loads, but are more complicated to install and more expensive.
| Feature | Single Phase Reactor | Three Phase Reactor |
| Power Source | Works with single phase voltage power | Works with three phase power |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency, more losses | Higher efficiency, less losses |
| Applications | Small scale power conditioning, household appliances | Industrial systems, motor drives, harmonic filtering |
| Installation | Simple wiring, easy setup | More complex wiring, requires expertise |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for small loads | Higher cost, designed for heavy duty applications |
| Load Handling | Handles lower power loads | Supports high power and continuous loads |
| Voltage Stability | More fluctuations, less stable | More stable, smoother power flow |
| Core Structure | Uses simple laminated iron core | Uses three leg or five leg core for better magnetic balance |
Figure 5-3 three phase degrees apart
Difference between Single Phase Inductors vs Three Phase Inductors
Single Phase Inductors vs Three Phase Inductors
Single phase inductors are suitable for low power electronic devices and voltage regulation. They have a simple structure, easy installation, and low cost, but they have low efficiency and high energy loss, and are suitable for light to medium loads. Three phase inductors are commonly used in industrial drives, electric vehicle charging, and power factor compensation. They can provide more stable current, reduce energy loss, and support higher power loads, but they are more complicated to install and more expensive.
| Feature | Single Phase Inductor | Three Phase Inductor |
| Power Source | Works with single phase electric power | Works with three phase in electricity |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency, higher losses | Higher efficiency, lower losses |
| Applications | Low power electronics, voltage regulation | Industrial drives, EV chargers, power factor correction |
| Installation | Simple single phase wiring, easy to install | More complex wiring, requires expertise |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for small scale use | Higher cost, designed for heavy loads |
| Load Handling | Handles light to moderate loads | Supports high power and continuous loads |
| Voltage Stability | More fluctuations, less stable | More stable, smoother power flow |
| Core Structure | Uses simple laminated iron core | Uses three leg or toroidal core for better magnetic efficiency |
Conclusion: Choosing Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power

Figure 6-1 1 phase vs 3 phase electricity
The choice between single phase electricity and three phase power supply depends on the specific application, power requirements, and efficiency considerations. 1 phase electricity remains suitable for residential and small commercial use, while 3 phase voltage power dominates industrial sectors, renewable energy, transportation, and high power applications. Understanding the differences between these power systems enables engineers and procurement professionals to make informed decisions when selecting electrical equipment and designing power distribution networks.
FQA
Which is better, 3 phase or single phase?
single or 3 phase: Three-phase power is better for high-power applications, offering better efficiency and stability. Single-phase is simpler and sufficient for homes and small businesses.
Is 240V single phase or 3 phase?
240V can be single-phase or three-phase, depending on the wiring. In residential areas, 240V is typically single-phase.
How do I know if I need single phase or three phase?
If you run household appliances or small business equipment, use single-phase. For heavy machinery or high-power industrial use, choose three-phase.
What are the benefits of 3 phase power?
Higher efficiency, smoother power delivery, reduced voltage drops, and better support for heavy loads.In the connection phase of the software integration, developers encounter several compatibility issues.
What are the disadvantages of 3 phase?
Higher installation and maintenance costs, complex wiring, and not necessary for low-power applications.Any mistake in the phase to phase connection may cause a short – circuit in the power supply system.
Can I run 3 AC on single phase?
It depends on the total power demand. If the combined load is too high, you may need three-phase power.
How to change 3 phase to single phase?
Use a transformer or phase converter to step down three-phase power to single-phase.
How to change single phase to three phase?
Use a rotary phase converter or VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) to convert single-phase power to three-phase.
How to get 3 phase power?
Contact your power utility provider to check availability. If not available, use a phase converter.
What is 0 phase electric
“0 phase” is not a standard term. You may be referring to the neutral wire or ground in a power system.
Can one of 3 phases be a different voltage
Ideally, no. Voltage imbalance can cause motor damage and inefficiency.
What is phase in electrical
Phase refers to the timing difference between AC voltage waveforms in a power system.
How is amperage divided in 3 phase circuit breaker
The total load is divided among three phases, reducing current per wire and improving efficiency.
How to wire a three phase electric motor
Connect each of the three motor terminals to the corresponding phase wires and ensure proper rotation direction.
Why is ac instead of dc power transmitted to buildings
AC is easier to step up/down with transformers, reducing transmission losses over long distances.


Pingback: ปั้มไลค์
Pingback: LSM SPORT