EV Charging System is becoming increasingly essential as the world shifts towards sustainable transportation. Key to their efficiency and reliability are transformers, which play a pivotal role in managing power quality, integrating renewable energy sources, and supporting fast charging stations. This blog delves into the critical functions of transformers in EV charging systems, highlighting their importance in ensuring seamless and efficient EV charging.

EV Charging System
Understanding EV Charging Systems
What is an EV Charging System?
An electric vehicle (EV) charging system is a set of devices and components designed to provide electric energy to recharge electric vehicles. These systems are crucial for the operation and widespread adoption of electric vehicles, offering a convenient and reliable way to ensure that EVs are always ready for use.
EV charging systems can vary in complexity, ranging from simple home chargers to sophisticated public charging stations. Home chargers are often installed in residential garages and are typically lower power, suitable for overnight charging. Public charging stations, on the other hand, can provide faster charging speeds and are strategically located in areas such as parking lots, shopping centers, and highways to facilitate long-distance travel.
The efficiency and effectiveness of an EV charging system depend on several factors, including the type of charger, the power output, and the compatibility with various EV models. As the demand for electric vehicles grows, the technology behind EV charging systems continues to evolve, aiming to provide faster, safer, and more efficient charging solutions.
What is an Electric Vehicle Charging Station?
An electric vehicle charging station, also known as an EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), is a physical device that supplies electric energy for the recharging of electric vehicles. These stations are the backbone of the EV charging infrastructure, making it possible for EV owners to recharge their vehicles conveniently and efficiently.
EV charging stations come in various types and configurations. Level 1 charging stations use a standard household outlet and provide the slowest charging speeds, making them suitable for home use. Level 2 charging stations offer faster charging speeds and are commonly found in public places and residential settings. DC fast chargers, or Level 3 chargers, provide the fastest charging speeds and are often located along highways and in urban areas to facilitate quick recharges.

Electric Vehicle Charging Station
The design and functionality of EV charging stations are continually improving. Innovations in charging technology, such as wireless charging and ultra-fast charging, are being developed to enhance user convenience and reduce charging times. Moreover, the integration of smart technologies allows for better energy management and user experience, making EV charging more accessible and efficient.
The Importance of EV Charging Stations
Electric vehicle charging stations play a pivotal role in the adoption of electric vehicles. Without a robust and widespread network of charging stations, the convenience and practicality of owning an EV would be significantly diminished. Charging stations provide the necessary infrastructure to support the growing number of EVs on the road, ensuring that drivers can recharge their vehicles whenever and wherever needed.
In addition to supporting individual EV owners, charging stations also contribute to broader environmental goals. By facilitating the use of electric vehicles, which produce zero tailpipe emissions, charging stations help reduce the overall carbon footprint and promote cleaner air quality. This transition to electric mobility is a critical component of global efforts to combat climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Public and private sectors are investing heavily in expanding the EV charging infrastructure. Governments are offering incentives and subsidies to encourage the installation of charging stations, while businesses are integrating EV chargers into their operations to attract environmentally conscious customers and employees. This collective effort is essential for creating a sustainable and efficient electric mobility ecosystem.
High-Frequency Transformers in EV Charging Systems
What are High-Frequency Transformers?
High-frequency transformers are a type of transformer that operates at higher frequencies than traditional power transformers. These transformers are designed to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, using high-frequency alternating currents. They are essential components in various electronic devices and systems, including EV charging stations.
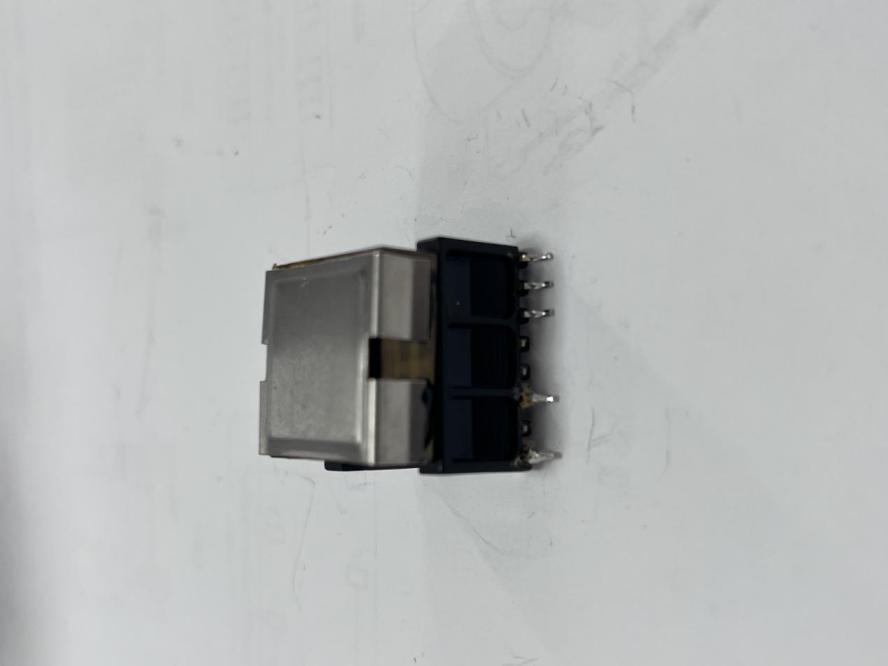

electric vehicle charging stations near me
The key advantage of high-frequency transformers is their ability to operate efficiently at higher frequencies, which allows for smaller and lighter designs compared to low-frequency transformers. This efficiency is achieved by reducing the core size and using materials that can handle high-frequency currents effectively. High-frequency transformers are commonly used in applications that require compact and efficient power conversion, such as power supplies, inverters, and EV charging systems.
The Role of High-Frequency Transformers in EV Charging Stations
High-frequency transformers play a crucial role in the operation and efficiency of electric vehicle charging stations near me. These transformers are used in the power conversion process, which is essential for converting the AC power from the grid into the DC power required to charge EV batteries. The high efficiency and compact size of high-frequency transformers make them ideal for use in modern EV charging stations.
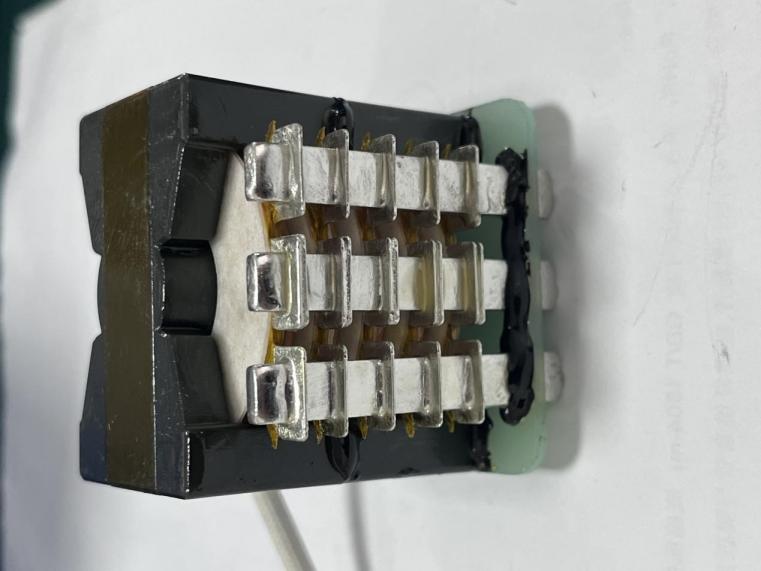

free electric vehicle charging stations
One of the primary functions of high-frequency transformers in free electric vehicle charging stations is to ensure efficient power conversion. By operating at high frequencies, these transformers can achieve higher efficiency levels, reducing energy losses during the conversion process. This efficiency is critical for minimizing the overall energy consumption of the charging station and providing faster charging times for EVs.
In addition to efficiency, high-frequency transformers also contribute to the safety and reliability of public electric vehicle charging stations. They provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, protecting both the vehicle and the charging station from electrical faults and surges. This isolation is essential for maintaining the integrity of the charging process and ensuring the safety of users and their vehicles.
Benefits of Using High-Frequency Transformers in EV Charging Systems
The integration of high-frequency transformers in EV charging systems offers several benefits that enhance the overall performance and user experience. Firstly, the compact size and lightweight nature of high-frequency transformers allow for more flexible and space-efficient designs. This flexibility is particularly important for public charging stations, where space constraints can be a significant challenge.
public electric vehicle charging stations
Secondly, the high efficiency of these transformers translates into reduced energy costs and lower operational expenses for charging station operators. By minimizing energy losses during power conversion, high-frequency transformers help optimize the energy usage of the charging station, making it more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Lastly, the use of high-frequency transformers in electric vehicle charge station supports the development of advanced charging technologies. Innovations such as ultra-fast charging and bidirectional charging (V2G) rely on efficient power conversion to function effectively. High-frequency transformers enable these technologies, paving the way for more sophisticated and user-friendly EV charging solutions.
Conclusion: Essential Role of Transformers in EV Charging
Transformers are integral to the efficient and safe operation of EV charging systems. They address the critical needs of voltage conversion, electrical isolation, and power distribution, ensuring that EV charging infrastructure can meet the growing demands of the market.


Pingback: เรียนต่อประเทศจีน